Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
51% Attacks for Rent — The Consequence of a Liquid Mining Market
In order to remain decentralized, cryptocurrencies using a proof of work system must not allow a single party to control the majority of total hashing power.
But as the global pool of hashing power grows more liquid, cryptocurrencies need to pass another important test. They must be able to resist an attack from the total rentable global hashing power for their specific algorithm. Otherwise, arbitrageurs may find it financially attractive to rent hashing power in order to perform 51% attacks.
There are a few things preventing this from happening:
- Algorithm-specific miners — Many rigs are optimized for a certain hashing algorithm, and switching to another, e.g. SHA-256 → X11, is unfeasible.
- Illiquid mining market — Most of the global hash power is illiquid and not rentable. Therefore, large upfront investment is required to build significant hashing power. The upfront cost for an attack is almost always not worth it.
- Opportunity cost — Cryptocurrencies are usually designed to heavily favor good actors by providing them with greater rewards for acting in the benefit of the entire network. Any attack must outweigh the risk of failure including loss of mining rewards, loss of reputation and damage to the network. Long-term miners do not want to destroy their future earning potential by successfully attacking a network, shaking market confidence, and causing the price to fall.
But times are changing. The mining market is becoming more liquid.
Why is the Liquid Mining Market Growing?
The increase of total hashing power in the long-run.
The long-run increase of cryptocurrency prices will incentivize miners to invest in hashing power until any incremental gain is equal to the cost. In other words, if the value of rewards continues to go up, or if the cost per unit of mining power decreases, miners will invest in more hashing power. Both of these are likely to happen in the long-run.
A higher percentage of hashing power will be for rent.
Buyers and sellers both benefit from the ability to rent and lend respectively. Separation of concern leads to higher degrees of specialization and increased operational efficiency. This is why hardware manufacturers sell their mining rigs and don’t mine themselves. If renters focus all of their time on finding opportunities with the highest amount of ROI, they are likely going to be the best at extracting value per unit of hashing power. Conversely, lenders can de-risk their business because their rental income is implicitly diversified across each entire hashing algorithm. In this world, lenders can simply focus on rental relations, asset utilization, and upkeep.
Rent-A-Miner Attacks Are Already Possible
Crypto51 calculates how much it would cost to rent enough hashing power to match the given network hashing power for an hour. NiceHash does not have enough hashing power for most larger coins, so this figure is sometimes theoretically above 100%.
Hash rates are from Mine the Coin, coin prices are from CoinMarketCap, and rental pricing is from NiceHash.
A few caveats:
- The quoted attack costs do not include the money you earn in the form of block rewards, so in many cases, the costs will actually be substantially lower.
- Crypto51 is quoting the spot price for what is available on NiceHash. In real life, the more you rent, the more expensive it will be because of supply & demand.
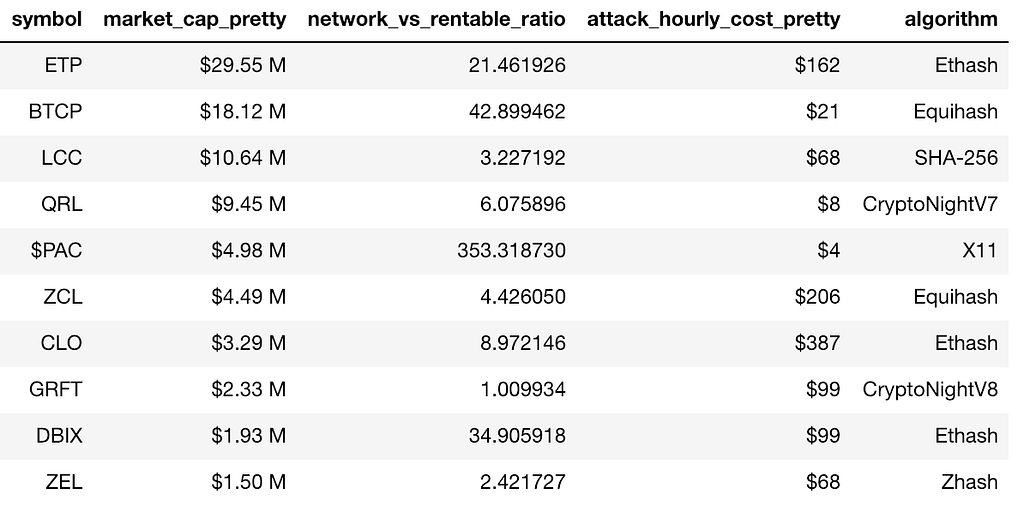
Coins Vulnerable to Rent-A-Miner Attacks
ETP is the #91 ranked coin on CMC. You can rent up to 21X the network’s hashing power. The cost of an attack is only $162 per hour. ETP/BTC and ETP/USD pairs are available on Bitfinex.
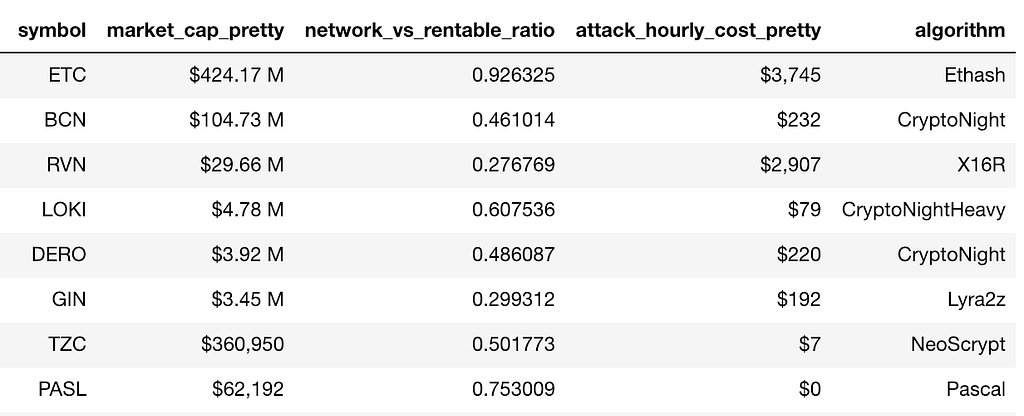
Vulnerable Coins Assuming 2x the Rental Capacity
Currently, these coins are out of reach since the total rental capacity available on NiceHash is not enough to fully match the network’s hashing power.
But let’s imagine the likely circumstance that NiceHash is able to 2x their total rental capacity. Now coins like ETC (rank 18), BCN (rank 40), are easily in reach.
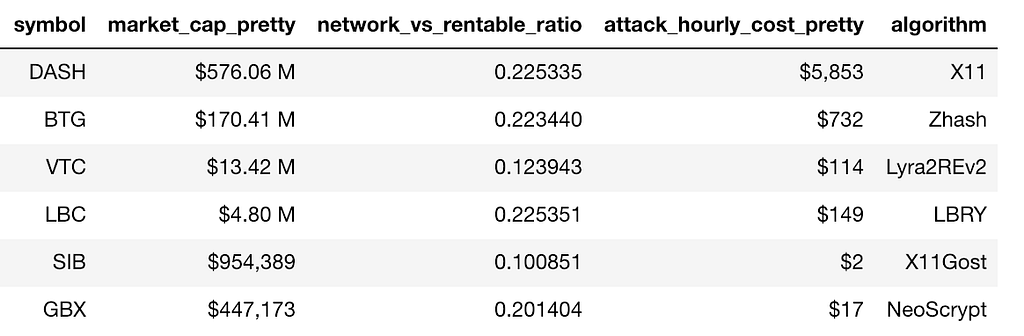
Vulnerable Coins Assuming 5x the Rental Capacity
A 5X increase in rental capacity puts coin like DASH (rank 15) and BTG (rank 28) in danger.
So what if 51% attacks are possible? How do attackers make money?
Fortunately, it’s impossible to ever create a transaction for a wallet that you do not own the private key to. But, controlling the majority hashing power means you can execute a double spend attack by temporarily reverting certain transactions on the ledger.
The Mechanics of a Double Spend Attack
When miners find a new block, they are supposed to broadcast this to all other miners so that they can verify it, and add a new block to the blockchain. However, a corrupt miner can create their own blockchain in stealth.
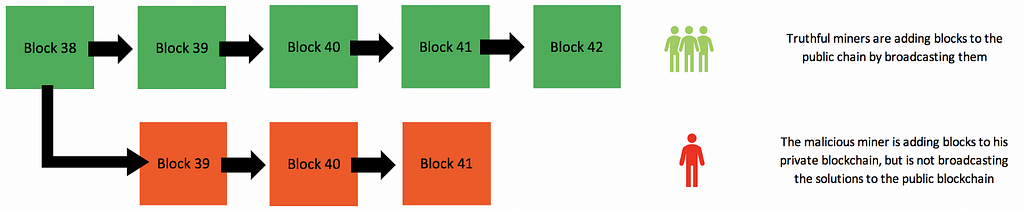 Graphic from Jimi S.’s Article on How 51% Attacks Work
Graphic from Jimi S.’s Article on How 51% Attacks Work
To execute a double-spend, the attacker will spend his or her coins on the truthful chain. But they will leave out these transactions on the stealth chain.
If the corrupted miner can build a longer chain faster than all the other miners on the network, they can broadcast the stealth chain to the rest of the network.
Because the protocol adheres to the longest chain, the newly broadcasted corrupt chain will become the de facto, truthful blockchain. The transaction history for the attacker’s previous spend will be erased.
Note that just because a miner controls 51% of hashing power, does not mean they will always have a longer chain. In long-run they will probably have a longer chain. To guarantee this in the short-run, an attacker would likely want to control closer to 80% of the network power.
Where to spend the coins? Exchanges are Likely the Target
For a double-spend to pay-off, you need to find a way to actually extract value from the spent coins. If you can’t spend the coins in the first place, there’s no point.
The most likely place an attacker would spend their coins on is an exchange because they are the single biggest buyers of various cryptocurrencies.
Here’s what the attack would look like:
- Choose a target network that looks profitable
- Accumulate a significant amount of coins on the target network
- Rent NiceHash hashing power and silently grow the stealth chain
- Trade these coins on an exchange for another currency e.g. BTC
- Withdraw BTC to another wallet.
- Broadcast the stealth chain to the network
- Get the initial coins back
- Repeat with a different exchange
How Exchanges will Likely Respond
As you can probably imagine, exchanges do not enjoy being bamboozled. If this kind of behavior becomes too costly for them, they will likely respond by increasing security surrounding withdrawal periods, deposit periods, and account verification.
Waiting longer for withdrawal will make it more costly for attackers, as they must then maintain the majority hashing power for longer. But this also draws the ire of legitimate traders and exchange users who already complain about the inordinate time it takes to get their cryptocurrencies out.
Another way exchanges may respond is by carefully screening coins that are so easily compromised. However, delisting coins also mean a reduction in trading volume and revenue. I hope this happens, because altcoins that are solely used for speculation, are in dire need of an existential threat.
Ultimately, we’ll likely see a combination of both. The harder it becomes to successfully get away with a double-spend attack, the less money an attacker can justify spending. In the long-run, the balance of these two forces will converge on some market equilibrium.
How Cryptocurrencies will Respond
Altcoins may find new ways to combat this threat by:
- Using more obscure algorithms for which there are few miners. This is at best a bandaid solution. Fewer miners for your algorithm means it’s difficult to grow your hashing power. If your network grows, then the algorithm will no longer be obscure.
- New projects may be to stake their security on the blockchains of larger networks. e.g. ERC20.
- Pushing for new consensus algorithms that are more resilient to 51% attacks e.g. proof of stake. POS isn’t perfect though and has challenges of its own.
Big is Beautiful
How much larger is the rental market going to grow? It’s not inconceivable to witness a 100x increase, so how many coins are really safe?
Coins with high market caps and low cost of attack are particularly fallible. Given that this is true, will the market respond accordingly by discounting insecure coins? Conversely, will the market place a premium on cryptocurrencies with mammoth mining networks?
To quote a Hacker News comment, “Rent-a-miner attacks seems like another amusing example of when the emergence of a market can break a system. Satoshi foresaw people trying to mount a 51% attack by buying a ton of machines, and so he went to great lengths to ensure this was unlikely using mining. I don’t think Satoshi foresaw the liquid AWS-like market for instant hashing power. The ability to mount a limited-time 51% attack makes the attack literally 1000x easier than a buy-machine 51% attack.”
About the Author
I quit my job recently to start HodlBot.
We automatically diversify and rebalance your cryptocurrency portfolio into the top 20 coins by market cap. Think of it as a long-term crypto-index that you can DIY on your own exchange account.
If you don’t want to index, you can also create a custom portfolio and let HodlBot rebalance it for you.
To get started all you need is a
- Binance Account
- $200 in any cryptocurrency
If you want to know how HodlBot indexes the market and completes rebalancing, check out the blog I wrote here.
51% Attacks for Rent — The Consequence of a Liquid Mining Market was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.