Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.

Are you trying to create a java spring boot application embedded with real time analytics? (WSO2 Siddhi). This article explains how to do exactly that by combining a fast, embed-able realtime analytics library with a immensely popular micro services platform, Spring Boot. As a bonus I will show you how to do that under 5 minutes using with code-generation !. After following this article you can generate a fully-fledged java spring boot project with a documented REST API , friendly,responsive front-end , basic spring security , comprehensive test coverage and database integration with just a few shell commands! The generated code will be your foundation for real time micro service/ application.
JHipster is a handy application generator that creates Spring Boot and Angular application. Jhipster is one of the best low code Development platform in open source community. Jhipster had become very popular Github with in short amount of time. It has a high performance java stack on the server side with spring boot and a front-end with angular,bootstrap and react. It makes project management easy with powerful workflow build tools like Yeoman, Webpack and Maven/Gradle. Many developers personally use it to generate multiple Spring microservices that are preconfigured to work in their company’s infrastructure. But this articles’ objective is not to give a detail explanation about Jhipster. This article will focus on how to create a Jhipster module for WSO2 Siddhi. If you are new to Jhipster or want to read more about Jhipster, please read {https://cbornet.github.io/}.
You may have some specific real time analytics (Siddhi) setup that you like to use in your Jhipster projects. Because you don’t want to reinvent your own wheel in every project, it makes sense to abstract all the boilerplate into your own generator. In that case you can build your own Jhipster generator for WSO2 siddhi and use it with your every Jhipster project.
In Xiges.io we encourage low code Development platform for our projects. Mainly we use architectural pattern which implements reusable solution to a commonly occurring problem in our the projects. So we implement code generation with Jhipster Modules and use with our Jhipster projects. This will also definitely kick start your Jhipster projects in your organization.
Getting set up
This section explains how to build the basic Jhipster generator module. If you already know how to create a jhipster module, you can skip this part and go to the next section.
A Jhipster module is a Yeoman generator. Also it is an NPM package. As a first step to generate a basic yeoman generator (which would eventually be our jhipster generator) install NodeJS .After that you’ll need to have Yeoman ,Yarn and Bower installed as well as the generator (yo) for creating generators.Please follow below commands with npm.
npm install -g generator-generator
npm install -g yeoman
npm install -g yo
To check whether Yeoman is installed correctly just type yo command in the command line which would list you all the installed generators. If you can find yeoman there, you are good to go. Finally make sure you have git installed.First create a new directory which you’ll write your jhipster generator. This directory must be name as generator-jhipster-<name of your module(Siddhi) > . Normally a Yeoman generator is prefixed with “generator-” but Jhipster modules are prefixed with “generator-jhipster-“. Executing the below commands in order would create the folder and generate the jhipster module template.
npm install -g generator-jhipster-module mkdir generator-jhipster-siddhi cd generator-jhipster-siddhi yo jhipster-module
This is not really a JHipster module, that is meant to not be used in a JHipster application. This module is used to generate a new template for coding a new JHipster module for Siddhi. A JHipster module to create a JHipster module. Answer the questions to generate the module, so we can implement the changes.
File structure
As you can see we have readme file and package.json for generator itself.Test folder holds tests for the generator. The index.js file is the entry point for the generator.It contains the template files for the boilerplate (for generating the actual scaffolding). We created the default generator. Now we can modify it and add the our custom features.
Scripting the Siddhi generator
now we will check how to customize the jhipster generator we created and add our own features in the generator with the following steps:
- Setup and import the generator-jhipster
The index.js file needs to export the generator-jhipster which will get run by Yeoman. Now I am going to clear the everything in our generator and start from the scratch. Here is what index.js file look after that.
const chalk = require(‘chalk’);const generator = require(‘yeoman-generator’);const packagejs = require(‘../../package.json’);
// Stores JHipster variablesconst jhipsterVar = { moduleName: ‘siddhi’ };// Stores JHipster functionsconst jhipsterFunc = {};module.exports = generator.extend({// all your yeoman code here
});
We assign the extended generator to module.exports make it available to the ecosystem. This is the typical method we use when we export modules in Node.js. Then we can have our own functionalities to perform through methods. In every method we added to the index.js is run once the generator is called and usually in sequence.Some method names have priority in this generator. The available priorities(in running order) are in order:
- initializing- Initialization of your methods.(getting configs and checking project current state )
- prompting — prompt user preferences for the options( call this.prompt()).
- configuring — Saving configurations and configure the project.
- default — If your method name doesn’t match priority and put into this group.
- writing — copy template-files to the output folder and parsing (routes, controllers, etc).
- conflicts — Handling the conflicts.
- install — Where installations are run and specially add maven dependencies to the target Jhipster project pom file. (npm, bower)
- end — Called last, cleanup.
After implementing these methods your file should be like this.
Jhipster module uses Composability, which is one of the main functionality in Yeoman. The “composeWith” (this.composeWith()) method in yeoman generators allows the generator to run parallel with another generator and it can use features from the other generator instead of having to do it all by itself. In this above example it composes with the “jhipster:modules” sub generator and get the access to Jhipster’s variables and functions.
As you can see in the code we add Jhipster function (under the install() phase) to add Maven dependencies into the pom.xml file (addMavenDependency). Also used Jhipster global variables. These are the short definition for each variable.
baseName: the name of the applicationpackageName: the Java package name
angularAppName: the AngularJS application namejavaDir: the directory for the Java application, including the package folderresourceDir: the directory containing the Java resources (always src/main/resources)webappDir: the directory containing the Web application (always src/main/webapp)
You can see java spring boot classes and resource files add to the writing()phase and it’s done by calling the template function(all the java spring boot classes described in the next section ) . If you interested in other functions available in Jhipster module please visit — https://cbornet.github.io/modules/creating_a_module.html.
2. Initializing the generator
We initialize our generator with package.json. In the above code Node invokes that require() function with a local file path as the function’s only argument and it gets the package.json file.This file is a Node.js module manifest. Our package.json file must contain the following.
I configured the following:
- yo: CLI tool for running Yeoman generators.
- generator-mocha: a generator for the mocha test-framework.
- gulp: a front-end build tool.
- mocha: mocha is a JavaScript test framework for Node.js programs.
3. Create gulp file
We use gulp file as our build system.Tools like Gulp are often referred to as “build tools” because they are tools for running the tasks for building a web application.Your gulp file must be look like this.
It’s often used to do front end tasks like:
- Spinning up a web server
- Reloading the browser automatically whenever a file is saved
- Using preprocessors like Sass or LESS
- Optimizing assets like CSS, JavaScript, and images
So now we finished the creating basics of jhipster generator for WSO2 Siddhi. But now we have to configure Spring boot with Real time analytics(WSO2 siddhi).
Spring boot + Real time analytics
Spring boot is very popular java-based framework for building web and enterprise based applications. Spring framework provides a wide variety of features addressing modern business needs. Spring boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade spring based applications that can “just run”. Spring boot take an opinionated view of spring platform and combining third party libraries so developer can start with minimum fuss. Most of spring boot applications need little bit of spring configuration. Because of this spring boot had become low code development platform. So Its easy to emebade WSO2 siddhi to spring boot. Lets see how how it’s done.
Before we go further we have to understand main concepts about real time analytics with WSO2 siddhi. WSO2 Siddhi is a java library which carry out real time processing on complex events.The streaming SQL Language of siddhi is being used to describe complex conditions from the data streams. Siddhi is able to perform both Stream and complex event processing. Below diagram shows basic workflow of the Siddhi 3.0.
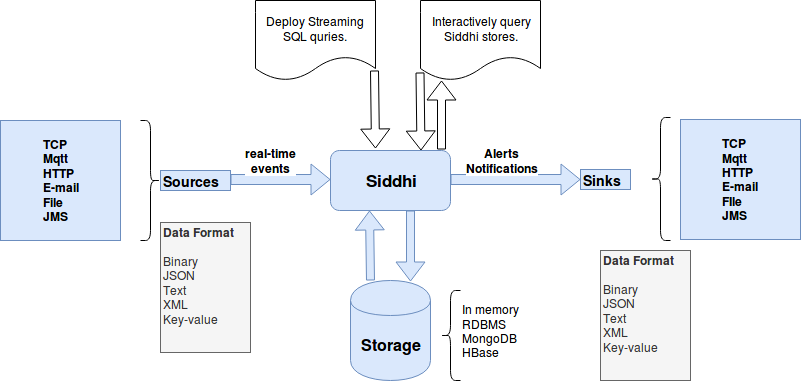 Basic workflow of the WSO2 Siddhi 3.0
Basic workflow of the WSO2 Siddhi 3.0
Now we are Embedding Siddhi in a Java Spring boot project and it allows you to use the Siddhi query language to carry out real time processing on complex events without running a WSO2 CEP server.
Implementing Business Service and adding POST Rest Service for Siddhi Application
As first step we need to define a stream definition and Siddhi query.Stream definition always define format of your incoming events and query defines as below.
String definition = "define stream TempStream(roomNo int, temperature double, deviceId long);"
String query = "@info(name = 'avgTemperature') " +"from TempStream#window.time(60 sec) " +"select avg(temperature) as temperature,deviceID " +"group by roomNo " +"insert into AvgTempStream ;";
Step 02: Creating Siddhi runtime
This step involves creating a runtime representation of a siddhiAppRuntime by combining the stream definition and the Siddhi query you created in Step one.
SiddhiManager siddhiManager = new SiddhiManager();//Generating runtimeSiddhiAppRuntime siddhiAppRuntime = siddhiManager .createSiddhiAppRuntime(definition+query);
The Siddhi Manager parses the siddhi App and provides you with a siddhi app runtime. This siddhi app runtime is used to add callbacks and input handlers to the siddhi app runtime.
Step 03: Registering a Callback
Siddhi has two types of callbacks.
- Stream Callback — this subscribes to an event stream
- Query Callback — this subscribe to a query
We need callback to retrieve output events from query. So we can register a callback to the siddhi app runtime. When results are generated, they are sent to the receive method of this callback. Also we can print the incoming events from an event printer which is added inside this callback.
ex-:
siddhiAppRuntime.addCallback("AvgTempStream", new QueryCallback() { @Override public void receive(Event[] events) { EventPrinter.print(events); } });Step 04: Sending events
As a final step you need to send events from the event stream to the query, you need to obtain an input handler as below example.
//Retrieving input handler to push events into Siddhi
InputHandler inputHandler =siddhiAppRuntime .getInputHandler("StockEventStream"); //Starting event processing
siddhiAppRuntime.start();
//Sending events to Siddhi
inputHandler.send(new Object[]{2, 23.0, 100L});Refer to these files at the bottom of the article for exact implementation of the Business Service and adding POST Rest Service for Siddhi Application.
Conclusion
Creating a JHipster module with WSO2 Siddhi is an easy way to simplify your microservice generation, especially if your microservice uses the same configuration. Since it is a module, it’s very easy to add functionalities and meet your needs. Our company Xiges Solutions uses this real time analytics for making real-time predictions and tracking with our IOT products.
Here is GitHub repository with the module used in this blog. Feel free to fork it and make changes to match your company requirements!
Now you can download jhipster generator for siddhi by using this command
npm install g generator-jhipster-siddhi
Then run the module on a jhipster generated application.
yo jhipster-siddhi
Soon this module will be available in the jhipster marketplace.(After JHipster team verifies it )
link for the source code- https://github.com/xiges/generator-jhipster-siddhi.
link for the npm registry- https://www.npmjs.com/package/generator-jhipster-siddhi.
If you got any suggestions or enhancements you want to see in the module please create an issue in the Xiges git hub repository — https://github.com/xiges/generator-jhipster-siddhi/issues
That’s all I have for this topic. Thanks for reading. Until next time!
References
- https://yeoman.io/authoring/composability.html
- https://www.jhipster.tech/modules/creating-a-module
- https://www.baeldung.com/jhipster
- https://yeoman.io/authoring/file-system.html
- https://gulpjs.com/docs/en/getting-started/javascript-and-gulpfiles
- https://siddhi-io.github.io/siddhi/#try-siddhi-with-wso2-stream-processor
- https://docs.wso2.com/display/CEP400/SiddhiQL+Guide+3.0
Lightweight real time analytics with Spring Boot + WSO2 Siddhi was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.