Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
The benefit of increased efficiencies and process improves make Blockchain appealing. GDPR is a compliance headache for corporations and governments.
Navigating how to use Personally Identifiable Information (PII) with blockchain can be difficult.
The big concern is the right to be forgotten. Immutable public ledgers make being forgotten nearly impossible.
If you understand Hyperledger Fabric, you’ll be able to keep PII off your blockchain.
GDPR Cheatsheet
What is it?
The General Data Protection Regulation unifies data privacy laws in the EU.
Why does it matter?
The cost of non-compliance is up to 4% of annual global turnover or 20 Million Euros, whichever is greater.
Who does it affect?
Any business that collects personal information on citizens of the EU i.e. anyone with a website.
When is it enforceable?
Now! The law came into effect on May 25th 2018.
Does it apply to all data?
No, you can’t use GDPR to get your bank to forget who you are, the bank still needs to comply with Anti Money Laundering laws.
What is Hyperledger?
At first the naming of Hyperledger projects can be a little confusing. Hyperledger is a Linux Foundation project and Hyperledger Fabric is a Hyperledger project.
What’s the relationship between the code base for Hyperledger Fabric and Hyperledger Indy?
There is none, they are independent projects.
Think Microsoft Excel and Microsoft Outlook. Two different projects that sit under the Microsoft umbrella.
What is Hyperledger Fabric?
Hyperledger Fabric is a private and permissioned blockchain network.
 Hyperledger Fabric is a blockchain image source
Hyperledger Fabric is a blockchain image source
Bitcoin is a public and permissionless blockchain. The main difference between the two is how trust is established. Bitcoin was designed for use in a trustless environment so it needs to assume bad actors. Bitcoin becomes more secure as the number of nodes in the network increases. Hyperledger Fabric networks have known participants that share a need to transact. As a result less nodes are required to secure the network.
Social Proof and why does it matter?
159 engineers from 28 organizations have contributed to Hyperledger Fabric
Including:
- Fujitsu (Japanese multinational information technology equipment and services company)
- GE (American multinational conglomerate)
- Hitachi (Japanese multinational conglomerate company)
- Huawei Technologies (Chinese multinational conglomerate which specialises in telecommunications equipment)
- IBM (American multinational information technology company)
- SAP (German multinational software corporation that makes enterprise software to manage business operations and customer relations)
Note the diversity of large multinational companies contributing.
This is important because it shows corporate buy-in.
“With more than 1,500 industry and technical experts, discover why IBM Blockchain Services is the place to start, accelerate and innovate your blockchain” — IBM
IBM is selling Hyperledger Fabric as an enterprise blockchain solution today.
Amazon offers Hyperledger Fabric as a service on AWS today.
Microsoft offers Hyperledger Fabric as a service on Azure today.
We are still in the early days of blockchain.
Enterprise ready technology is a big deal.
Private Data
Hyperledger supports having many blockchains in the same network. Each blockchain has its own channel, only members of the channel can view the blockchain. Not every member of a channel needs to see the business logic or data for every transaction.
A private data collection can be used to keep data confidential. Only the members authorized in the chaincode (smart contract) receive the data.
Private data gets sent peer to peer between authorized organizations.
channels keep transactions private from the broader network whereas collections keep data private between subsets of organizations on the channel.
Hyperledger Fabric’s Noteworthy Features
- There is one immutable ledger for each channel.
- Each peer has a copy of the ledger for each channel they are a member. A peer can be a member of multiple channels.
- Chaincode gets instantiated on a channel. This makes everyone in the channel aware of the chaincode’s interface. The chaincode must be installed on a node for the node to be able to run it. Not every node needs to have the chaincode installed.
- Peers expose a set of APIs to interact with the services that they provide.
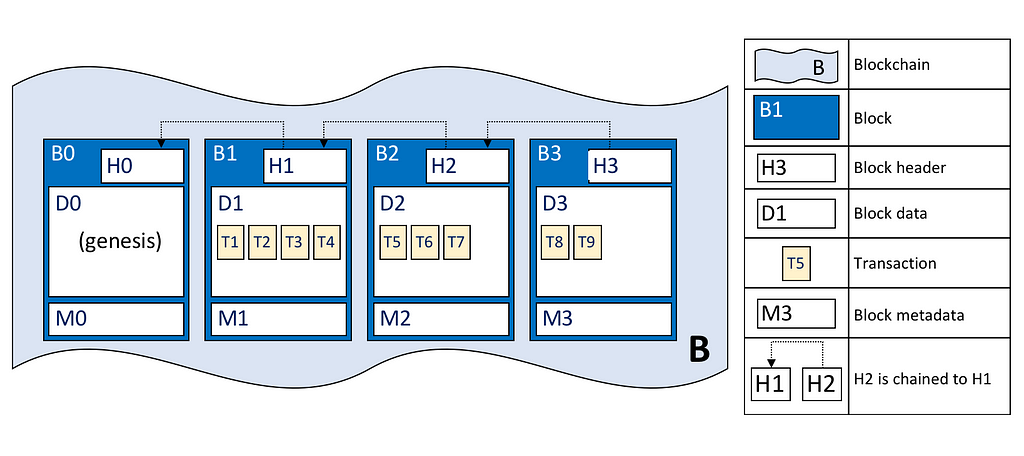
Hyperledger Fabric Cheat Sheet
Hyperledger Fabric - the 20 most important terms made simple
How to get blockchain’s benefits in a world governed by GDPR. was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.