Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
0chain describes itself as the “worlds fastest enterprise blockchain.” The company provides a combination of blockchain-as-a-service and decentralized cloud storage to enterprises wishing to adopt blockchain solutions. The 0chain protocol is self-forking, meaning 0chain is completely customizable to the requirements of different organizations, which can use it to create dapps designed to serve their own needs. 0chain is super-fast, processing 1000 transactions per second.
The protocol was conceived out of a recognition of the current problem set with existing blockchain including scalability and energy consumption. It runs on a unique consensus protocol with different parties called miners, sharders, and blobbers participating in block production. Miners generate the blocks, sharders store the blocks, and blobbers store unstructured data for web and IoT applications.
The company has recently announced a partnership with Amazon Web Services (AWS) and is about to launch its mainnet. We recently had a chance to catch up with three of the 0chain team to discuss these developments.
Saswata Basu (SB) is a founder and co-author of the 0chain white paper. Phil Castillo (PC)) joined 0chain in July this year as Chief Revenue Officer from his last role in Hewlett Packard. Derick Fieberger (DF) is 0chains Operations Director, alongside his role as Founder/Chief Investment Officer at Arturo Capital.

(L-R) Basu, Castillo, and Fieberger from 0chain
Here’s what they had to say:
0chain recently announced it has achieved the Standard Partnership Certification with the AWS Partner Network. For our readers, can you explain in more detail what this means? What’s the scope of the interaction between AWS and 0chain and how is this beneficial for each party?
PC: Our AWS Standard Partnership is one small piece of our relationship with AWS and enables 0chain to be marketed as an AWS solution partner to their thousands of customers.
Our devnet today is built on AWS. When companies use 0chain’s blockchain, this benefits AWS as it means the likely consumption of their cloud services. We are one of the first companies providing not only blockchain-as-a-service but also decentralized storage via blockchain which is very appealing to AWS and their customers.
We are working on the Advanced level partnership and have numerous conversations and touch points with AWS on a number of different fronts promoting our joint solution. They have been very generous investing in us and defraying much of the cost of our existing global cloud consumption. Custom forks of our blockchain will likely be created leveraging enterprise-grade service providers like AWS. As a result, miners and blobbers don’t need to invest in specialized hardware to participate with 0chain and can leverage AWS and other cloud solution providers.
0chain also partners with other crypto- and blockchain-based projects such as Bitclave and NEO. Can you provide more details about how these partnerships work?
SB: The partnerships with these projects are to enable applications to use the 0chain platform to store, read, and monetize their data automatically without having to write elaborate smart contracts. Aside from high reliability, availability, and faster performance, the 0chain protocol will provide transparency of data reads and writes, and enable disbursement to different entities associated with the data.
DF: There are several angles we can approach a partnership with a crypto project and provide benefits. For simplicity’s sake, we can focus on our dCloud, which is our most popular innovation. How can dCloud help a crypto project? In order for a public ledger or a decentralized application to operate properly – in most cases – it must utilize enterprise-grade hardware to accommodate the storage and compute demands of the protocol or application. Also in most cases, dapps and validators are using the public cloud to address these storage demands. 0chain will offer a decentralized public cloud solution. Since crypto is very focused on preserving decentralization, offering a decentralized cloud (dCloud) in place of the standard public cloud, at less cost without sacrificing performance provides a very appealing offering to these projects. This is why several crypto projects have already sought us out.
Many enterprise-standard blockchains have come under fire within the blockchain community for failing to deliver on the promise of decentralization. How do you feel about this? How does 0chain operate in a way that allows it to balance decentralization against the privacy, scalability, and the resilience requirements of an enterprise-level distributed ledger?
PC: The criticisms of current 1.0 blockchain solutions are understandable, some are even block-less environments and others don’t fully encompass blockchain’s core decentralized benefits as you have pointed out.
At 0chain we saw the need for a truly enterprise-class, ultra-fast, fully featured blockchain with added innovations relative to storage via blockchain. So we built ours from the ground up. One of our core differentiators is that our primary go to market system is a public, fully decentralized blockchain (our mainnet) that is designed for miners, blobbers, and sharders to participate independently.
We have unhooked the need for specialized mining hardware so miners/blobbers may leverage any cloud infrastructure they choose. Another attractive offer for enterprises is the ability to fork from our mainnet and create a custom dApp. In these instances, an enterprise can customize the miner profiles and other parameters to suit their applications’ needs. Miners and blobbers will be encouraged to participate in building consensus and providing storage for these forks and thus be decentralized.
SB: Of the privacy, scalability, and resilient requirements of an enterprise ledger, the latter two are inherent in our system, and in fact, we are better.
By decoupling miners, sharders, blobbers we’ve made our network faster, more scalable, and more resilient to failure or any Byzantine condition. The privacy part of the requirement can be implemented through smart contracts, and this will provide a faster and more secure execution of the transaction than using Hyperledger or Corda channel constructs.
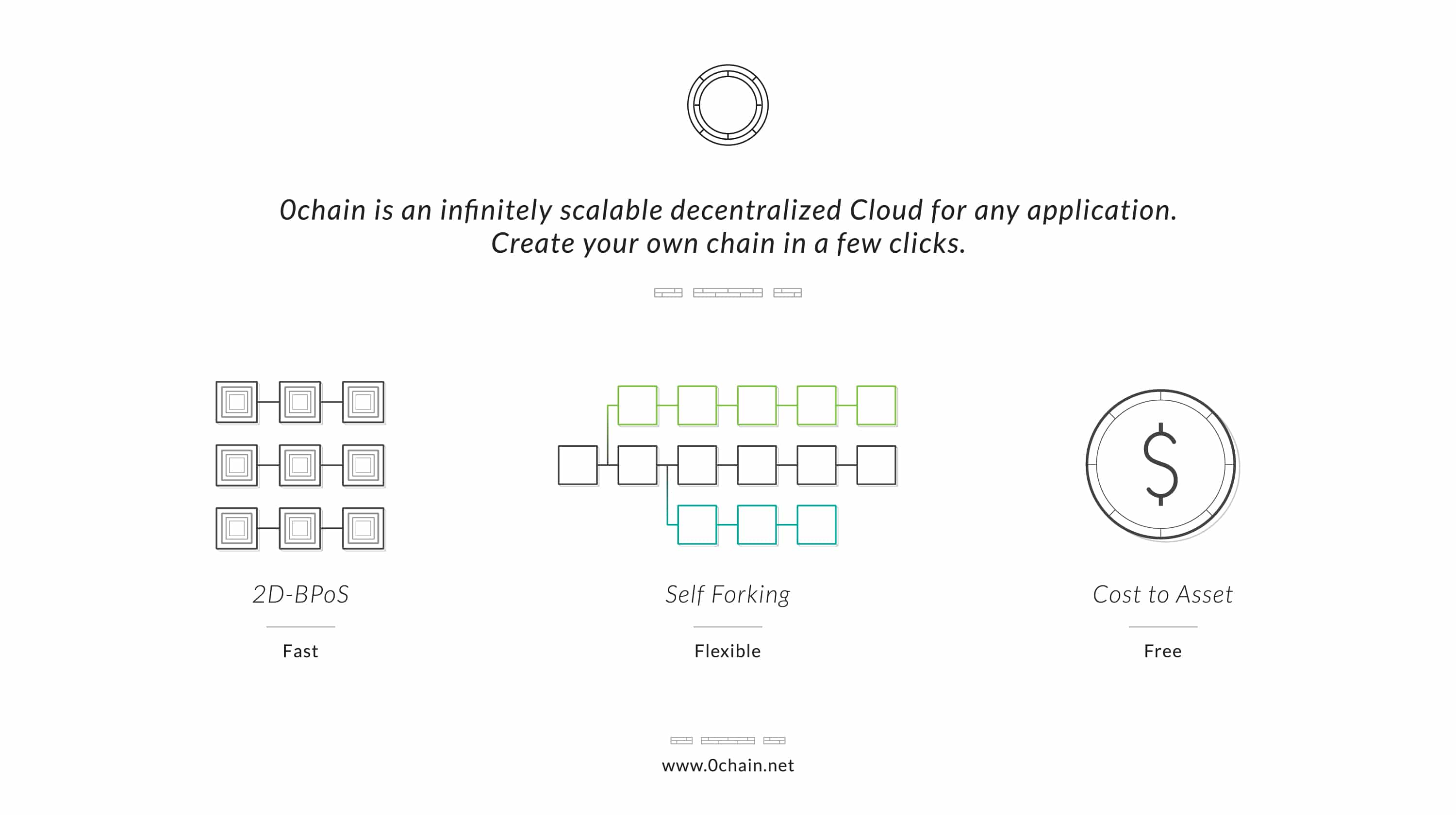
A mini-explainer of how 0chain works
Blockchain-as-a-service is a pretty broad scope. Can you tell us what kind of clients you foresee being the first ones to take up the 0chain BaaS offering?
PC: Some of our conversations currently include:
Solution providers wanting to add blockchain as an immutable record for storing JSON IoT data from sensors on cold storage trucks. With 0chain, they are able to quickly provide real-time food safety data in case of recalls, or other uses.
Another company is using our solution to provide a layer of secured data storage, tracking all reads/writes, to deliver permissioned access for a portion of their storage.
We also see interest in companies wanting to have their own service storing data via a wallet that enables better control over privacy, security, and economics compared to Dropbox or Box.
BaaS is pretty straightforward, but when you add in being able to store JSON and other small datasets on the chain or storing large data sets via blockchain, it allows for the creation of many new and emerging uses.
One of the main blockers to enterprise adoption of blockchain is privacy and confidentiality – particularly in the financial sector. How does 0chain seek to assure potential clients that data held in its public blockchains is protected against hacks, and cloaked with the necessary confidentiality?
SB: 0chain has a secure software wallet, the first of its kind, to prevent hacks to companies’ tokens or data. Additionally, enterprises can encrypt their data to protect their privacy. 0chain’s blockchain platform enables users to track writes and reads to provider further transparency regarding any access to their data.
Recent blog posts indicate that the 0chain PoS consensus protocol is still under testing. Can you provide us with a brief overview of how the consensus protocol will work and the anticipated transaction speeds?
SB: We are a variant of DFinity consensus, where we have a smaller active set that is shuffled based on stake from the pool. The pool is not connected to the network, but connects during the shuffling rounds and syncs up with the network. Additionally, we have optimized our communication mechanism to provide faster finality. Furthermore, our consensus is achieved based on a count-and-stake model to enable a higher level of security. Shortly, we will release our consensus protocol paper and will explain all these aspects in detail.
How can miners or other service providers get involved in the 0chain network?
PC: We welcome all miners, sharders, and blobbers to reach out to us via our Telegram channel or directly at zero@0chain.net. Service providers are best to contact me (Phil Castillo), our CRO, at phil@0chain.net and can learn more about us at www.0chain.net.
0chain is purposely designed to be self-forking so that enterprises can have a blockchain that meets their specific requirements. Can you explain (as non-technically as possible) how this works in practice to ensure sustainability? Is there any risk of decreasing the size of the miner pools from having multiple chains?
PC: Simply put, adding forks increases the opportunity for miners and blobbers, without diluting the size of the miner pool. They will be able to participate in mainnet as well as forks where appropriate and receive ZCN in either cases.
SB: The self-forking aspect of our architecture allows us to grow infinitely, and we expect the miner/sharder/blobber pool and their infrastructure to grow linearly with demand.
The 2018/2019 roadmap seems to indicate that all hands are on deck to put the mainnet live. At that time, a token swap will happen once 0chain is no longer using ERC20 tokens. How are the mainnet development efforts progressing? What are the main challenges and focus areas for 0chain to achieve its goals in putting the mainnet live?
SB: We are very close to launching mainnet and our main focus is now implementing the storage protocol, miner protocol, and token economics. We have had very good performance on our core blockchain with billions of transactions completed in our test-net. We have an early version of the storage protocol implemented and have been showing it privately.
Before our mainnet goes live, we will do a token swap from ERC-20 to native 0chain tokens.
If widespread/mainstream adoption of blockchain is the goal, what do you see are the important next steps to achieve this within businesses and other enterprises?
PC: Blockchain by itself as a transactional system has some interesting 1.0 use cases in supply chain tracking, collapsing financial processes, and a few others.
When storage of small data sets (i.e. IoT) can be accomplished on chain or storage of petabytes of data via chain is understood by enterprises, there will be a host of new and more widely adoptable use cases.
Decentralized storage via blockchain provides an immutable record of all data stored, allows tracking of all reads/writes, permissioned access, and CDN like performance based on multiple parallel paths for data to traverse.
Decentralized storage and cloud are bound to revolutionize the business environment but we will have to show enterprise customers, pilot and then publicize the results to see wide adoption. Having partnerships with trusted cloud providers adds credibility to our solution, lowers the barrier to entry with conservative enterprises while not sacrificing the decentralized and immutable attributes of blockchain.
Thanks, Saswata, Phil and Derick, for your insights and good luck with the launch!
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.