Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
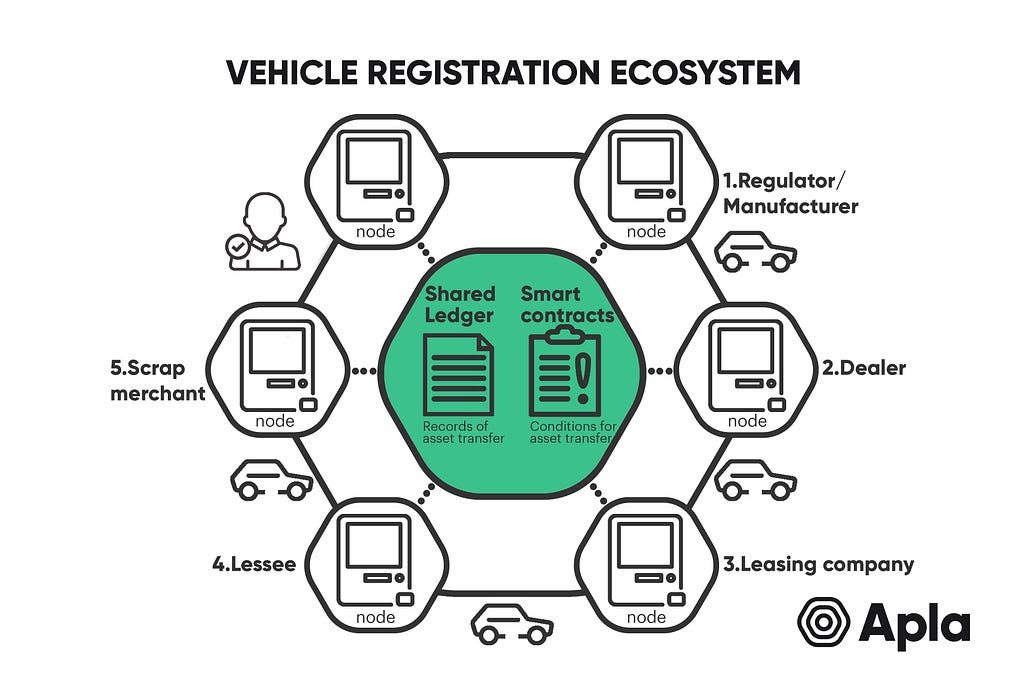
As one of the most technologically advanced and sophisticated industries in the world, the automotive industry is at the forefront of innovation, applying technologies which range across carbon-neutral electric motors, self-driving cars and integration with the Internet of Things.
Concurrently, industry participants face efficiency problems in customer service and operations that bring about unnecessary costs and increased prices for goods and services within the automotive industry. These inflated costs pass on to vehicle owners, corporate vehicle service users, etc.
Reports from LMC Automotive and Technavio show that new and used car markets worldwide are close to being equal when considered in terms of the number of units sold. In 2016, the total number of used car sales was estimated at 90 million units for the year. However, buyers of used cars experience a lack of trust on the secondary market for vehicles: there is uncertainty regarding the car’s history and this issue cannot be completely resolved even by conducting costly vehicle inspections.
Car Manufacturers Losing Out
Warranties are not uncommon in the automotive industry, allowing consumers an added layer of protection from faulty vehicles, whilst also giving credibility to manufacturers. However, provision of warranties for vehicles is a costly business.
Analysis from Warrantyweek.com in 2016 showed that car warranty costs throughout the world stood at $56 billion in 2016, whilst they exceeded $61 billion a year earlier. Moreover, 30% of the total warranty costs finds its origins in poor practices and processes amongst dealers. Whilst it should be noted that the highest warranty costs are in Europe and North America — with lower figures in Asia — there is much room for bringing warranty costs down..
A 2016 McKinsey & Company report on blockchain in insurance estimated that 5–10% of all insurance claims worldwide are fraudulent. Furthermore, issuance and servicing of policies, in addition to claim management account for a sizeable 39% of total insurance costs. This size of this figure can be put down to the fact that the majority of insurance companies use arcane methods when issuing policies and managing claims, resulting in high operational cost inefficiencies.
Aside from warranty claims counterfeit spare parts have a detrimental impact on the automotive industry, with fake spares being most prevalent developing countries. The scale of the problem is highlighted by the fact that the Federal Trade Commission of United States estimates the market for counterfeit vehicle parts at approximately $12 billion annually.
All in all, losses on part of counterfeiting, warranties and insurance claims can be estimated at $100 billion, with these cost passed on to the consumer.
Blockchain: Technology of Efficiency
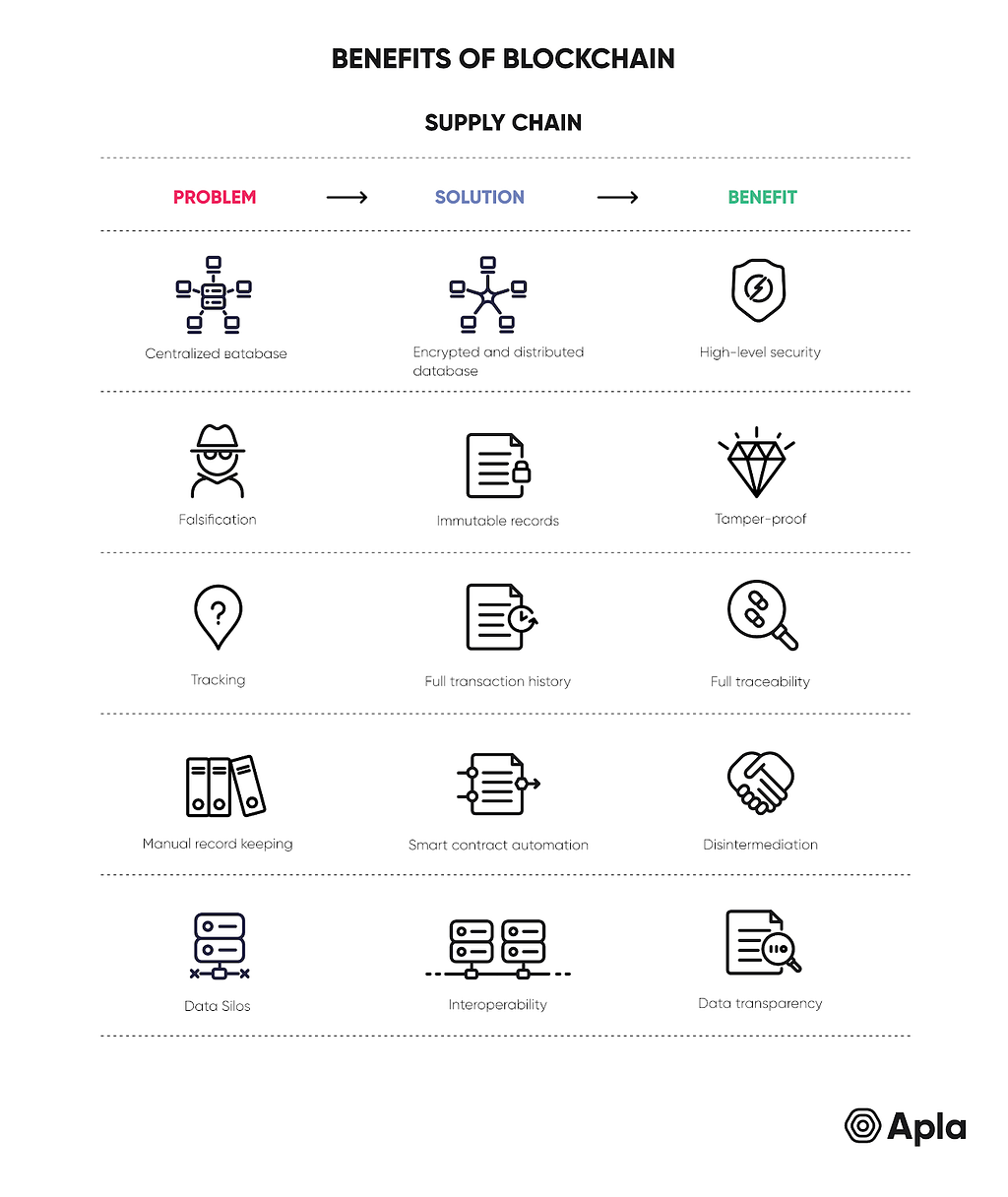
Bearing the costly pain points highlighted above in mind, data integrity and records being kept fully up to date become the most important aspects in the interactions between different participants of the automotive industry.
Data accuracy coupled with the inability to arbitrarily tamper with records (data immutability) therefore becomes essential for:
- Maximizing vehicle resale value;
- Determining spare parts’ authenticity;
- Achieving increased accuracy and cost efficiency in insurance claim management;
- Optimizing insurance operations;
- Monitoring compliance with regulations and recommendations made by business partners; and
- Enforcing contractual relations.
As a transparent and secure technology, blockchain offers benefits which heighten data integrity. This is down to its tamper-proof nature since a blockchain-based record system not only stores data transactions chronologically, but uses a complex cryptographic signature to ensure that each transaction is irrevocably linked to the previous one, thereby rendering the database immutable.
Moreover, the ability to access current state records in real time brings about the opportunity to optimize operations, which translated into such spare parts inventory management amongst distributors becomes more robust and leads to better forecasting in repair shops about the parts they will need.
Increased Cost Efficiencies
Blockchain could eliminate the 30% of the total warranty costs which are accounted for by poor practices could be eliminated by implementing warranty management in which all claims, spare parts stock and time spent repairing vehicles is recorded within a single database. Depending on their status, stakeholders would have read or write access to this database and processes could be evaluated as a whole to see where inefficiencies can be ironed out. Moreover, the key point here is the traceability of objects and actions at each step of the process.
As an example, warranties from vehicle manufacturers are subject to vehicle owners carrying out maintenance through certified garages using authentic spare parts. By doing so, the vehicle owner has a valid and irrefutable service and maintenance record for their vehicle from approved repair garages, with the records demonstrating the exact provenance of parts used. This process is crucial for a warranty to be considered valid and utilising blockchain throughout this process would give more credence to the data.
Key Benefits for Stakeholders
- Vehicle Manufacturers
- Data integrity of maintenance records and spare parts
- Reduction in warranty costs
- Insurers
- Policy price optimisation
- Reduction in claims management costs
- Vehicle Owner
- Increased trust in used-car market
- Transparent car history
- Maximisation of resale value
In addition to a reduction in administrative costs via disintermediation and process automation via smart contracts, blockchain also provides opportunities that will increase fraud detection and bring about new, innovative insurance products and services. As noted above, distributed ledger technology on which blockchain is based gives insurers and third parties instant and simple access to data (e.g. evidence, claim forms, police reports, etc.). By putting its insurance processes on a blockchain, an insurers could reduce claims regulation costs by up 30 percent.
The implementation of blockchain to the automotive industry is likely to lead to a significant reduction in costs and inefficiencies for consumers and businesses alike, with knock-on effects for other activities which are related and dependent on the usage of vehicle transportation. As such, the integration of blockchain could prospectively save billions of dollars annually.
Originally published by TechBullion here.
Adam is a tech enthusiast with a passion for everything blockchain and works as Apla’s content lead. With an educational background in technology law and innovation management, Adam has been working in digital content for the past five years.
Blockchain Business Review from Apla provides high-quality educational material from the world of blockchain to inform the business community of the competitive advantage that can be gained by integrating distributed ledger data storage within organizations. Our mission is to promote knowledge about blockchain and its uses in both the private and public sector and demonstrate the value of blockchain integration.
The Potential Blockchain Effect on the Automotive Industry was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.