Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
 Why Is Privacy Important?
Why Is Privacy Important?
So you think you have nothing to hide…think again. If you truly don’t see the value in keeping your data private, consider this: Post all your credit card numbers, bank account numbers, social security numbers, medical records and text messages on Facebook.
Are you willing to do this? Probably not.
But if you aren’t careful or are targeted by a hacker or another malicious actor, this could happen. Your data could be stolen and posted publicly on the internet, despite your own objection. The problem with privacy is that people don’t see its value until they lose control of their personal data, and then it’s too late.
If you take precautions to protect all your information, responsible privacy practices will become second nature for you.
Why Is Internet Privacy A Problem?
Do you want to be able to keep certain information private on the internet?
I think most people would agree that it is in their best interest to be able to keep some information to themselves on the web. So then why is privacy on the internet such a debated topic?
A lack of privacy isn’t always bad. Many of the most popular internet products and services rely on collecting massive amounts of data about people and using it to add convenience. The big companies that use your data (Facebook, Google, etc.) are big advocates against privacy protection because their business models rely on collecting and processing as much of your data as possible.
Unfortunately companies like Facebook and Google have such massive user-bases that it’s difficult to convince anyone to use more privacy-friendly alternative products. While it’s in users’ best interests to have control over their data and how it’s used, this is rarely the case.
Privacy, although it has made it into mainstream media recently, is looked-at as a niche issue that is for tech savvy people only. Although they are less popular than other services, privacy-friendly products exist, and some are very easy to use.
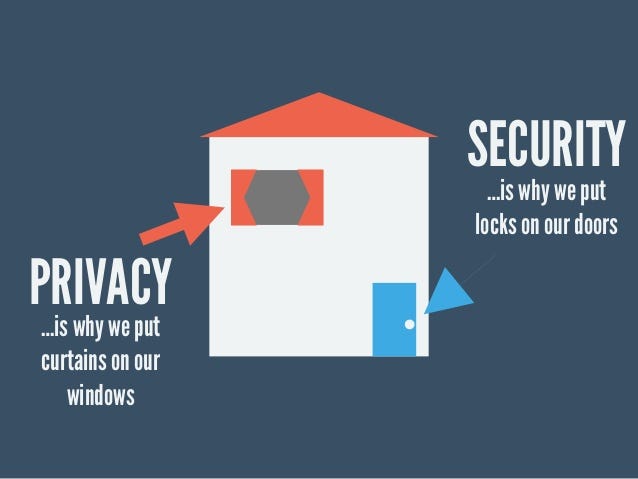 Source: https://wikity.readwriterespond.com/privacy-vs-security/
Source: https://wikity.readwriterespond.com/privacy-vs-security/
Security vs. Privacy: What’s the Difference?
Security and privacy are closely related, but are actually quite different. A service could be very secure, but could not be private at all.
What is Privacy?
Privacy refers to a situation where you, or your data, are free from being observed or disturbed by other people. Control over who can access your data plays a big role here. If you want to have true privacy, you need to be able to control who can access your information
“The right to control other’s access to one’s personal world, whether psychologically or physically. This can be attained by physical barriers or by communicating boundaries verbally.”What is Security?
Security is related to protecting and keeping unwanted parties from accessing your information. While privacy is more about keeping unwanted eyes off of certain data, security is about keeping the information private, after it has been collected.
It is not up to a privacy program to state the technology or processes to be used to protect personal information; it is up to the security specialists to make this determination. Source: CSO From IDG
Privacy is more about personal comfort levels — so how much information are you comfortable sharing. If you have privacy, then you are sharing a level of information that is in your comfort zone. Security then, is how the organizations storing your data protect it.
How To Maintain Your Privacy on The Internet
Use a VPN
VPNs are popular tools for bypassing school and office internet censorship. However, they also offer privacy protection for their users (hence the name, Virtual Private Network). These tools essentially move your internet connection to a different location so that you aren’t easily identifiable to the websites that track you.
By combining a trustworthy VPN with other privacy tools, you can take your privacy protection to an even higher level.
Create and Use Strong Passwords
Your password is your first line of defense against malicious actors who are trying to access your accounts. Don’t use passwords that are easily guessed (e.g. ‘password1’). Use passwords that are long and use a mixture of letters, numbers and symbols. It’s also a good idea to avoid using your name or other information that people could easily in your passwords.
Use Password Managers
If you’re using unique complex passwords for all the services and websites you log in to, it can be difficult to remember them all. Password managers can solve this problem for you. They can generate long passwords and store them all in a secure way so you don’t have to remember them yourself.
KeePass is a good option, as it uses password or key file authentication. Other popular password managers are LastPass and Apple’s Keychain.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Two-factor authentication means you need another factor beyond your password to log in to a given account. This could be a code sent to you via text message or email. This second layer of protection can protect you if your passwords get compromised in any way.
Encrypt Everything
Encryption is essential for keeping your personal data safe on the internet. It works by scrambling, or ‘encrypting’, anything you send over your network. This prevents anyone monitoring network activity from viewing the information you enter on sites you visit.
Read More: What is Encryption and How Does It Work?
For Local Privacy, Use Incognito/Private Browsing Modes
It’s a misconception that Google Chrome’s Incognito Mode or Mozilla Firefox’s Private Browsing Mode keep your browsing completely private. However, if you want to keep you’re using the internet on a shared or public computer these private browsing modes can help keep the next person on the computer from viewing your browsing activity.
Read More: Chrome’s Incognito Mode isn’t Private, So What’s the Point?
Use Tracker Blockers
Most of the websites on the internet use some sort of tracking or analytics platform. These trackers let the websites track the effectiveness of their marketing and get information about how many people visit their site. Unfortunately, these trackers also collect information about you, like your IP address, location and device type.
Read More: The Best Browser Extensions for Privacy
Use Ad Blockers
Ad blockers are similar to tracker blockers because they work by detecting ads on pages and block them from loading. In addition to protecting you from any data collection that these ads may do, ad blockers can speed up load times on the websites you visit.
Use Encrypted Messaging Services
While it may be more difficult to keep your communication private online, there are a few companies providing top-notch messaging products with a heavy focus on privacy. ProtonMail and Hushmail both offer email services that are totally encrypted and privacy-friendly.
For private messaging, use services like Signal, Telegram or Wickr.
Read More: Private Email & Messaging Platforms for Confidential Communication
Use HTTPS Everywhere
HTTPS encryption protects your data that you enter on websites from being transmitted over your network in readable, plain text form. Check the URL of the sites you visit and make sure they are HTTPS before you enter any information that you don’t want other people possibly access.
- https — Website is secure
- http — Website is NOT secure
Clear Your Cookies Regularly
Cookies are small text files that get stored on your computer. They contain small bits of information related to your web browsing and your device. Websites you visit use cookies to keep you logged in on the site so that if you navigate away from and come back to the site you don’t have to log in every time. While cookies add convenience to browsing they also open you up to unwanted tracking.
Be Cautious About the Permissions You Give Apps
When you download an app on your phone, it probably asks you to give certain permissions. Pay attention when accepting these terms, as the app may be asking for unnecessary access to your camera or microphone.
Giving an app permissions without being aware of what you’re consenting to could lead to accidental privacy breaches.
Minimize Your Social Media Use
While Facebook, Instagram, Twitter and other social networks may seem like a convenient way to communicate with your friends, they actually collect a lot of data about you.
Facebook operates one of the largest advertising networks in the world, and it uses all the data you share to serve you with targeted ads. You can limit the data profile that Facebook stores about you by only sharing required information.
Access the Web with TOR
TOR (The Onion Router) is a software that works similar to a VPN. It protects you by “bouncing your communications around a distributed network of relays run by volunteers all around the world.” Tor actually offers more privacy than a VPN because it doesn’t allow any of the nodes your signal passes through to see your IP address.
Tor is also available as a browser that applies the technology without you needing to install any software.
Update Your Apps, OS and Devices Often
Updates often contain important security patches and bug fixes, so you should download them as soon as possible. As software and hardware get older, there is a higher probability that a security flaw has come up. By keeping both software and hardware up to date, you add additional privacy protection.
Use Alternatives to Google
Google offers a wide range of web based services, but Google collects information about you and your use of the products when you use them.
This guide by Restore Privacy gives alternatives to most of Google’s products that you may use: Alternatives to Google Products — The Complete List
Use Private Search Engines
Generally private search engines don’t collect information about you or your searches. These are the most popular private search engines on the internet:
The Best Private Search Engines — Alternatives to Google
Use Private Browsers
Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, Microsoft Edge…there are a lot of options available for browsers. Not all browsers work the same though. For privacy and security, others are miles ahead.
Chrome is a great option if security is what you’re after, but it also shares your internet activity with Google. This makes Chrome a secure option, but not a private one. The best browsers for privacy according to Express VPN are Tor Browser, Mozilla Firefox and Brave.
Use Web Version of Facebook Instead of the App
When you install the Facebook app on your iOS or Android device, you give more tracking abilities to the social network. If you need to access Facebook from your mobile device, it’s better to just use your browser and go to Facebook.com that way.
This keeps Facebook from tracking your location and other key data points without you realizing it.
Be Careful with IoT (Internet of Things) Devices like Amazon Echo
IoT devices, like Amazon Echo, Google Home, and Apple HomePod are cool and new technology. People are buying them like crazy. What many people don’t realize or care to think about is how much more data they are giving to big tech companies when they bring these devices into their homes.
There have already been issues with these devices sharing information with the wrong people and as more and more people buy them, the privacy implications just grow more serious.
Use Virtual Machines
Virtual machines are like using a separate computer, except that they are contained on your computer. If you are using your computer to complete a sensitive task, or one where the privacy implications are higher, virtual machines can isolate it from other privacy threats on your normal computer.
Avoid Public Wi-Fi If Possible
Public Wi-Fi is a great convenience but it can also be a threat to your privacy.
- Man-in-the-Middle attacks — These attacks are when someone is able to access the connection between your computer and a website. This allows them to view your web activity without you knowing.
- Unencrypted networks — On these networks, your information is sent in plain-text, rather than in encrypted form. This means anyone with access to the network and see what is sent back and forth between your computer and the network.
- Malware distribution — Because anyone can access these networks, hackers may use public WiFi to inject malware onto your computer, without you noticing.
- Snooping and sniffing — Snooping and sniffing uses software kits and devices to allow someone to eavesdrop on WiFi signals. This allows for hackers to access your log in credentials and other information you may enter into a webpage.
Don’t Forget About Privacy on Mobile Devices
There is a misconception that privacy is mostly a threat on your computer. But because of the complexity and capabilities of smartphones, there are many, if not more, privacy threats on your phone than on your computer. One of these being location tracking. Because we’re more likely to carry our phones with us at all times, that gives companies considerably more information to collect.
Only Download Files from Trusted Sources
This one could be a no-brainer but you shouldn’t download files or programs from a website that you’re unfamiliar with. These files could contain malware or viruses. These unwanted programs could then be running malware in the background on your computer and collecting your private data without your knowledge.
Which Information Are You Protecting?
- Metadata: Metadata is the descriptive information about your devices and communications on your network. While this data doesn’t reveal the content of your communications, it can give away other information like your location and device type.
- Passwords: If your passwords get hacked or leaked you could be giving unwanted third-parties access to your accounts. This could include your bank accounts and social media accounts.
- Financial Information: If you store payment information in non-secure ways, you could share your data. The big concerns with losing financial information is that it actually can and will lead to financial loss.
- Medical Records: Your medical records could contain sensitive information that is in your best interest to keep private. If for example your insurance company could access your medical records they could charge you more for your coverage if your records contained a condition you hadn’t disclosed.
- Communication: This includes text messages, messages sent through messaging apps and emails. Your online communications probably contain sensitive information that you would prefer to keep private.
Who Are You Protecting Yourself From?
Hackers
The term “hacker” is definitely overused to the point that the term’s meaning is a bit cloudy. However, hackers are individuals trying to gain access to your information for personal or political gain. These cyber-criminals use a number of methods but their motivation is mainly getting your financial information, passwords, or social security number. They then use this information for identity theft or to access your bank accounts.
Advertisers
Much of the internet is built around advertising. To make their ads more effective or to get insight into how you interact with their websites, companies and businesses use the massive amounts of data they collect.
Google operates the largest advertising network in the world. With its analytics software and advertisements on a majority of the internet’s websites, Google knows a lot about you. If the idea of one company knowing most of what you do on the internet makes you uncomfortable, you are not alone.
NSA & Other Governmental Groups
Unfortunately, governments around the world have decided they need to track their citizens on the internet and through other means. Edward Snowden revealing the NSA’s surveillance methods shocked many people. In countries under authoritarian regimes, this is sadly the norm.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs)
The companies who provide internet service also monitor how people use the web. Congress passed a bill that allows ISPs to sell data about their user’s habits on the internet. This could lead to your browsing data ending up in third parties’ hands. ISPs can arguably access the most information about you because they see all of your internet activity, not just the browsing on specific websites.
Is It Really Possible to Use the Internet Privately?
Is Privacy Possible on The Internet?
Privacy and security on the internet are constantly evolving. What keeps you safe now may totally change tomorrow. Because the internet is an open platform, new threats emerge all the time. Technology and opinions surrounding it are constantly changing. It’s important to get second (and third) opinions on the products you use and the protection measures you take.
Your privacy is in your hands. Good luck!
Internet Privacy Guide — Keeping Your Data Safe Online was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.