Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
Based on our in-house research, and our personal experience, we’ve seen that a lot of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) businesses setup Google Analytics on their Website, then they move on. They add a blog, a subdomain with another service, and the data gets tangled up and becomes hard to exploit.
Google Analytics may not be the best platform to analyze activation, retention or monetization, but it has a lot of great features, and it can be setup in minutes.
There’s limited down-side to setting up Google Analytics in your App or on your Website, well… when integrated properly.
I wrote the following guide to help you setup Google Analytics in your App and on your Website. It’s based on our current setup at Highlights, and my previous experiences at LANDR and Greencopper.
How to Setup Google Analytics
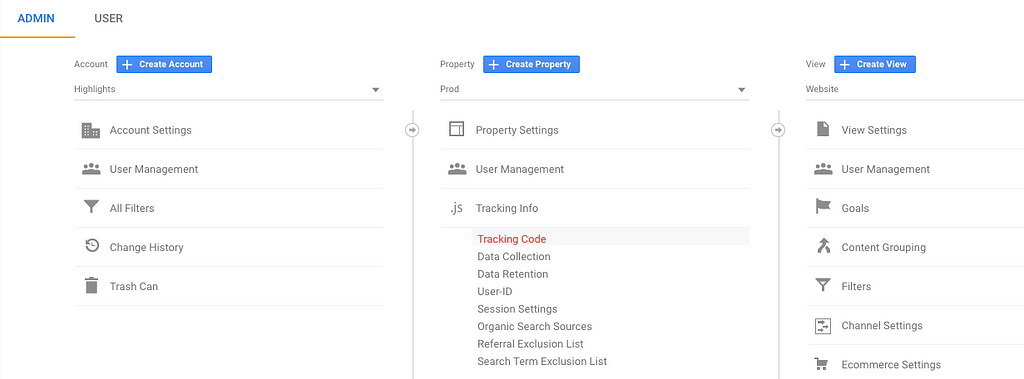
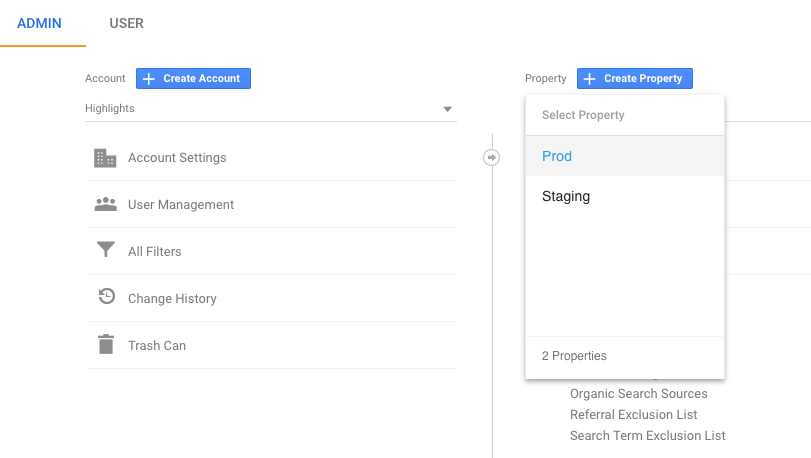
The first thing you want to do is to go to the Admin section of your Google Analytics account. From there, select your account.
 Google Analytics — Admin Panel
Google Analytics — Admin Panel
An account can have several “Property”. And properties can contain one or multiple “View”:
- A “Property” is used fo a specific project (it can regroup a Website, a mobile app, a blog, etc). It’s where you get your tracking code.
- A “View” filters information based on several properties. It’s what you select in Google Analytics from the dashboard view. By default, a single — unfiltered — view is created for a property.
It’s good practice to create 2 properties for a company that has both Staging and Production environments. It helps keep the Production data clean (no bad events, pageviews, or outdated setups).
For Highlights, we use 2 distinct tracking codes. One for Prod, and another one for Staging.
 Google Analytics — Tracking Codes
Google Analytics — Tracking Codes
How to Filter Your SaaS App Data
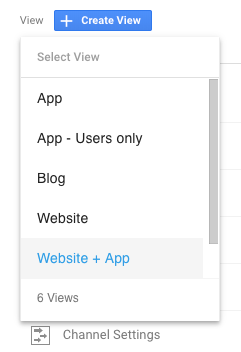
Once you have a Production property, you can split your traffic using several “Views”. At Highlights, there are 4 views that we use:
- App → For https://app.gethighlights.co
- App — Users Only → To exclusively track the authenticated users of https://app.gethighlights.co
- Website → For https://www.gethighlights.co
- Website + App → To track all sessions and users in a single bucket.
These views allow us to analyze in isolation the Website and Blog pages (“Website” view), the events from our App users (“App — Users Only” view), or the conversion from the Website to the App (“Website + App” view).
Unfortunately, when you create a new view, you can’t bring back the historical data; the view won’t contain any data.
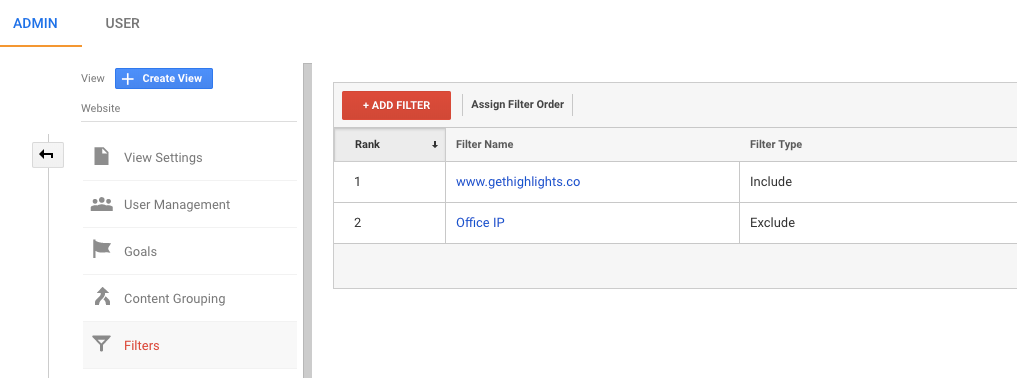
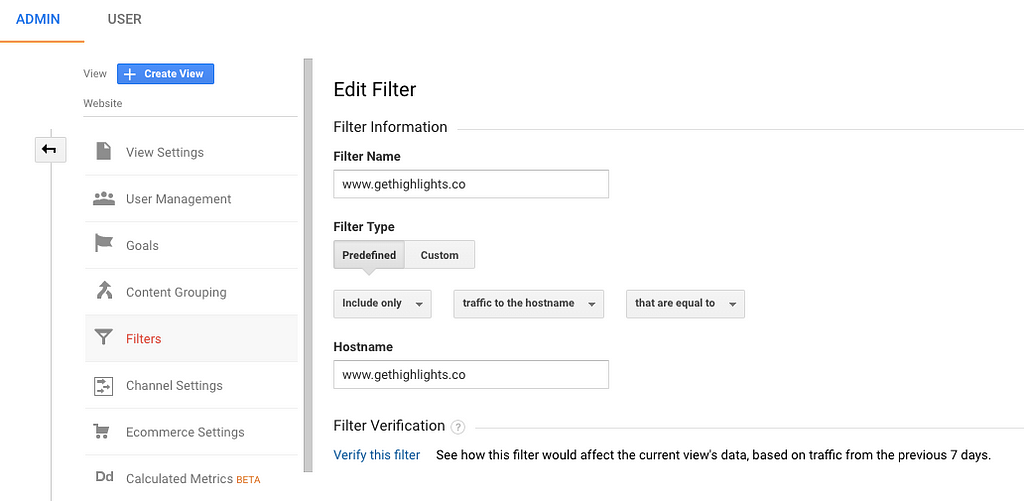
Once your views are created, you can add filters. A filter is a set of rules that will limit, or exclude some traffic / events / users from being sent to this view. For example, for Highlights we exclude our main office’s IP address, and only include the traffic from the “www.gethighlights.co” hostname for the “Website” View (Filter “Predefined” > “Traffic to the hostname” > “Equal to”).
When setting up filters, you can click on the “Verify this filter” link to check if the filtering is working. Google Analytics will indicate the percentage of users or pageviews impacted by the filter.
Here’s the configuration of the filter for the view “Website”. It only contains the traffic from “www.gethighlights.co”.
And below is the configuration of the filter for the view “App” that only includes the App traffic on “app.gethighlights.co”.
How to Integrate Google Analytics in Your App
The easiest way to setup Google Analytics on your Website and in your App is by adding the Javascript tracking code of a property to your web pages (at the bottom). It’s the easiest way, but also the least flexible.
 Javascript Tracking Code — Highlights
Javascript Tracking Code — Highlights
For Highlights, we use Google Tag Manager. GTM allows us to add events and different analytics tracking codes (Intercom, Drift, Amplitude, etc) without even opening the code editor.
It makes it easy to collect data from multiple tracking pixels with a single tag (the Google Tag Manager tag). It also provides a certain level of quality control for our analytics, which is useful when we’re making a lot of changes to the product.
Although Google Tag Manager can be used by anyone within the team to add tags and events, it needs to be set up by a developer (or a data specialist).
An interesting alternative to GTM is Segment. Segment also makes it easy to import and send to multiple integrations like Google Analytics. It has great features like data playback.
The main downside for Segment is that it’s costly, and that the price increases when you get more users and data. As a bootstrapped startup, we just can’t afford it yet. :-).
You can decide to start with Google Analytics as your main analytics platform, and when your team feels like conducting deeper analysis, or runs into limitations (the free version of GA is limited to 10M hits per month, GA uses data sampling, GA has no support, etc), you can consider transitioning to another analytics platform.
Analytics tools like Amplitude, Hotjar or Heap all have advantages when compared with Google Analytics. We’ll cover these alternatives in another post. Sign up to our newsletter to make sure you don’t miss out 👇.
Originally published at www.gethighlights.co.
How to Setup Google Analytics for Your SaaS App was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.