Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
𝙷𝚊𝚌𝚔𝚒𝚗𝚐 𝙷𝚞𝚖𝚊𝚗 𝙱𝚒𝚘𝚕𝚘𝚐𝚢
From Agriculture to Inter⌁Connection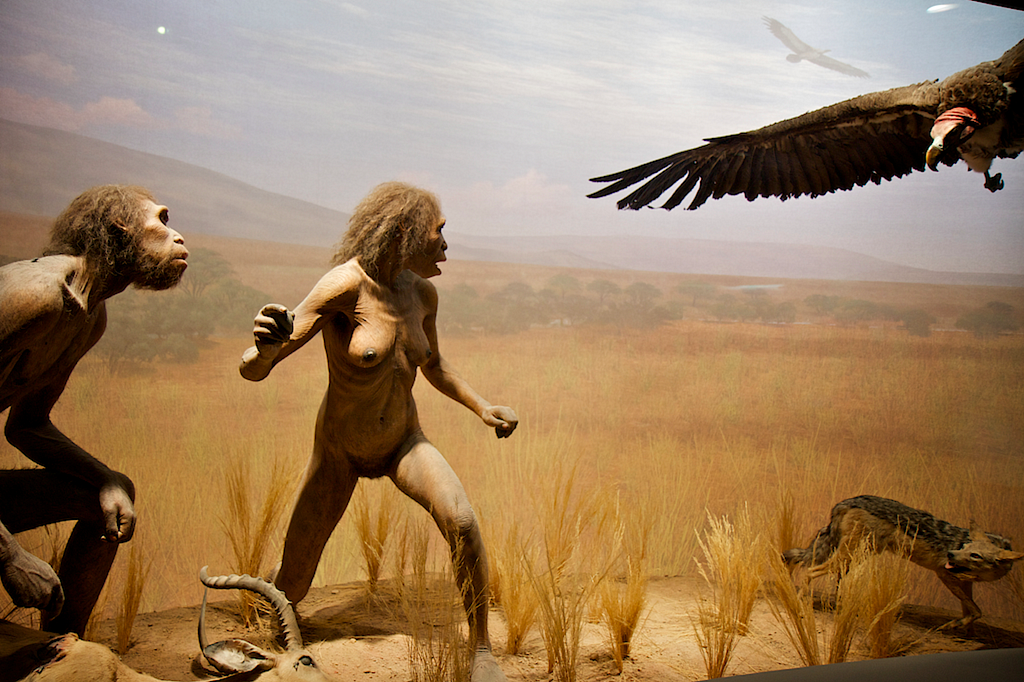 Mankey vs Mandibuzz vs Growlithe
Mankey vs Mandibuzz vs Growlithe
This is the story of the Homo Sapiens..✍️
In roughly 8,000 BC, humankind made a mistake that it wouldn’t fully digest for almost 10,000 years. It was a mistake that, both then and now, felt like the genesis of our species’ intellect, but may turn out to be a most unfortunate Faustian Bargain.
When a period of heavy global warming turned Middle Eastern soil into a bed of nutritious minerals, we, the self proclaimed “wise men,” could not resist temptation. We walked on two feet, swung our enormous brains about with reckless abandon, and slapped our hands together with bellies full of joy. We had done the impossible. We had mastered mother nature. Right?
“Not so fast!” Mother nature said, in her cryptic and indiscernible way. “As hunter gatherers, you are happy, you are healthy, and you value your tribes! You are free men in the truest sense of the word.”
Of course, we did not listen. Instead, we switched on the three mysteriously brilliant pounds of meat and began farming.
“Such a pity,” she said, shaking her head. “Laziness today is the poison of tomorrow. And antidotes take many thousands of years to find…”
In a sense, the Agricultural Revolution was our first misstep and we have been building upon a cracked foundation ever since. It’s not realistic to expect mankind to uproot itself and become intergalactic hunter-gatherers, just like we expect New York City to gut and renovate it’s ailing subway system. However, incremental changes can be made. In the next section, I’ll try to reconcile what those changes are and how they could possibly be be made
 Sorry I forgot how to color for a sec
Sorry I forgot how to color for a sec
🤝 THE WHEAT BARGAIN 🤝
beware the walnuts and pears planted for heirs
Around 8,500 BC, the wild, enigmatic, foraging men of the Middle East recognized a sobering truth: it was possible to harness Earth’s ability to cultivate food rather than trekking hundreds of miles in search of food. “Brilliant!” “Harmless!” “Necessary!” we thought. But, as we would soon find out, all this thinking and clumsy head swinging had paralyzing and unforeseeable consequences.
The domestication of the food supply bubbled into an unnatural population explosion and provoked a need for tremendously more abundant food sources and laborers. While the Neolithic Agricultural Revolution allowed men to become stationary beings for the first time in Homo Sapiens history, this decision was made without the understanding of why it had never settled down in its previous 190,000 years of existence.
According to Yuval Noah Harari, the beings who set the agricultural pendulum in motion were “neither kings nor priests, nor merchants. The culprits were a handful of plants. We did not domesticate wheat. It domesticated us.” When wheat wanted water, humans nourished it. When wheat suffered from disease, humans nursed it. When wheat was hungry, humans nurtured it. And thus, as the number of wheat stalks increased, so too did the newest species of ape.
The domestication of humanity by wheat is just one of many examples where one organism came to rely upon the fiercely upon another. The microbes in the human gut rely just as heavily on us as we rely on it. Amoeba floating in the sea both need eating as well as need to be eaten by minnows. Tuna need cleaner fish just as much as cleaner fish need tuna for waste. Planet Earth has a suspicious history of leaning two species against one another in order to facilitate evolutionary growth. So to speak, mankind’s unrelenting reliance on wheat and other staple crops pitted it in a Faustian bargain. Except this bargain didn’t last a few years. It lasted 10,000 (and counting)
The currency of evolution is neither hunger nor pain but rather copies of DNA helixes. If no more DNA copies remain, the species is extinct, just as a company with-out money is bankrupt. If a species boasts many DNA copies, it is a success, and the species flourishes. From such a perspective, 1,000 copies are always better than a hundred copies. This is the essence of the Agricultural Revolution: the ability to keep more people alive under worse conditions. ~Yuval Noah Harari
Interestingly, this vicious cycle did not occur in isolation. The crops which became, and have remained to be, our most important dilatants — wheat, rice, barley, and potatoes — seemed to colonize humans across the globe. Of course, it’s easy to criticize through the looking glass of revisionist history, pointing out negative residue as it was inflicted by the new. However, in our more self-conscious era of humanity, we can take refuge in the fact that most of documented history is now available. We can follow the trends and question with guarded skepticism everything that has not withstood the test of time. For the first men in Asia, North America, Australia, and basically all of planet Earth, Agriculture was a way to make life easier. What are we doing now that makes life easier?
The law of least effort dictates that people invariably gravitate to the least cognitively and/or physically demanding task~Daniel Kahneman (Touuch. Touch. Touch.)
(Touuch. Touch. Touch.)
✂A GOOD PAIR OF SCISSORS
is too easy to find
Shortcuts make for long delays~JRR Tolkein
A young lady once said “There’s nothing better than a good pair of scissors. Ones that are sharp and sturdy and cut through cardboard with little effort.” Human innovation is like these scissors. Each year, humanity improves the blades so that it can cut corners ever so slightly cleaner. Instead of pulling a tractors ourselves, we enslaved animals. Instead of walking from town to town, we built machines. Instead of calculating difficult math, we mad computers. The list is never ending.
Man’s genius is just a sharp pair of scissors and our whetstone is anything that we can manipulate.
Human history is bloodied with a toxic yearning to be smarter than not just all other species, but also the men of one, one-hundred, and one-thousand years prior. Agricultural farmers were smarter than nomads. Religious establishments were smarter than tribal ones. Industrial assembly-liners were smarter than artisans. Slavers were smarter than sharecroppers.
So who are we smarter than? Are technologists smarter than warmongers? Coders smarter than writers? Designers smarter than artists?
Nassim Nicholas Taleb often warns to be wary of neomania, or the adoption of new things for new things sake. Often times, man will leap head and foot prematurely into the newest swell, hoping for it to further decrease the demand on our bodies, unaware that this really is stirring up noxious fallout for the years to come. Just look at the list above. Agriculture destroyed our health. Religion drove apart our civilizations. Industrialism polluted our planet.
Who knows what’s next?️ ️
We may be the wise species, but we certainly don’t. So into the ether weeeeeeeeeeeeee go 🎢
 Somewhere, deep down there, Satoshi is hiding.
Somewhere, deep down there, Satoshi is hiding.
VERBUM SAPIENTI SAT
A word is enough for a Wiseman 🤔
Man was once a wholesome beast that raced through his country concerned with nothing other than his family, his safety, and what type of berries he would consume for dinner. Today, we throw away half eaten caviar and drink gin from mason jars. Our days of foraging are long lost, but the biological underpinnings have not changed. “The knowing ones” will always forage for more knowledge — it’s where the information comes from which changes.
In 10,000 BC, nomads foraged for information from their environments in order to find food, mates, and to protect their families. In 2017, with bellies full of frozen yogurt and gluten free pizza, Sapiens transduce the biological need to forage into scraping through (trash)bins of social media archives. Then, it moves twitchily onto the next patch. This new-old phenomenon, according to Doctor Adam Gazzaley, is an extension of Homo Sapiens ancestral food-foraging habits “where the perpetual sources of nourishment are websites, email programs, and iPhones.”
Herein lies the most troubling, but germane problem with today’s constantly stimulated mind:
People no longer need to worry about navigation, multiplication, and sometimes even relationships. Instead, we fill that open space with an orchard of tempting technological “information patches.” This idea, illustrated in the MVT model outlines the inherent discord between the ancient human brains and its modern-day goals.
…The next 40 years will bring us some wonderful things. I don’t mean to imply they’re all to be avoided. Alcohol is a dangerous drug, but I’d rather live in a world with wine than one without. Most people can coexist with alcohol; but you have to be careful. More things we like will mean more things we have to be careful about.~Paul Graham (Founder of Y Combinator)
One-hundred years ago cigarettes were healthy and cocaine was a prescription drug. Before that, we stuck leeches on ourselves, drained blood from our bodies, and performed ridiculous trepanning surgeries. The world is a completely and utterly befuddling place.
Who knows what we’re doing that’s killing us?
Now, we will enter into the discussion of a few things that I don’t think are killing us per say, but are certainly hurting our brains and our attention spans.
THE CORONATION ☯F PRIVATIZATION
on privatizing personal space
Whether it be walking through a crowded train station, sitting in a busy café, or merely working quietly from one’s own apartment, the concept of privacy and publicity has been garbled by technology. Once upon a time, eating in a crowded restaurant was by definition: public. Writing an essay in your bedroom: private. But now, we are confused. At any given moment, one can escape feelings of privacy and publicness through a refuge in their pocket or on their lap.
It has never been easier to run away from ourselvesThich Nhat Hanh
So, in a world more depressed than ever, is escapism a good thing?
Still though, we can’t blame new technologies for the entirety of the skyrocketing rates of dpression and suicide. It’s more likely that we were on this path far before Steve Jobs gave us the iPhone and maybe even before Henry Ford invented the automobile. Perhaps, our unhappiness is a confluence of every decision humans have ever made, or far scarier, perhaps it’s hard-wired into our DNA
However, there is an underlying beauty in instantaneous connection and communication. Yes, it may be wickedly hard for us to detach ourselves from toxic technologies int he present moment, yet the mere fact that I am able to stream these thoughts to you from an apartment in San Francisco is freighted with positive upshot.
Remember Zika?
People worried that the disease would become an explosive pandemic and that we were years away from a cure. That was 2016.
What the story of Zika shows is just how powerful human connectivity can be. While the cognitive load on the
The Agricultural Revolution was a rigid Pandora’s box. Once it was opened, there was no turning back. Industrialism was much the same story. However, both both have been improved by engineering and renewable technologies. So, perhaps, the Connection Revolution is freighted with the power to dismantle itself — or at least edit its own code. Technology may be a constellation of distraction and cognitive load for us all, but it also allows brilliant people from all over the world to come together and synthesize new ideas. That’s something we have never seen before in history.
Collaboration has become so easy, that it is sometimes considered distracting. Unless there is some technological Don Corleone playing puppet master over our attention, there is no reason to believe that we will not use the connective tools at our disposal to jettison ourselves from the rut into the next phase of tech-phoria
And I think we will. If you are looking for answers, the last part of this essay isn’t for you, but if you like thinking about tough questions, maybe it is.
To Homo Technicae
we go? 🚀
Human “ingenuity” is often the cause of our pain; yet, we can be encouraged by the fact that the rapid growth of technology also shortens our time spent in a cognitive rut. It took 10,000 years for us to realize that maybe the Hunter-Gatherers had the right diet, 2,000 to recognize that religion is only as good as its freedom, 150 to acknowledge the damage emissions have on our planet, and 20 to uncover the dangers of a constantly connection economy.
As always, we end with more questions than answers:
How long will it take for man to determine his own “technological paleo diet”?Will we be the ones to discover it?What will be the next tragic vice? Virtual Reality? Space Travel? AI powered laziness? Blockchain powered laziness?Is it this very self-inflicting cycle that which makes us human? Can we outrun it?
Are we in the midst of a change from Homo Sapiens to Homo Technicae?
Judge a man by his questions rather than by his answers-Voltaire
In the foreseeable future though, we’ll continue to have far more questions than answers. So, for now I’ll say:Let’s stay vigilant. We can’t let the wheat domesticate us.
Homo Technicae and his Mother Nature was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.