Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
The Mighty Bitmain
Bitmain, formally known as Bitmain Technologies Ltd., is a bitcoin miner, designer of ASIC chips, and operator of one of the largest Bitcoin mining pools headquartered in Beijing, China.
If you keep up with cryptocurrency news, you’ve probably heard the name Bitmain by now. Some people seem to love Bitmain, some say it’s evil, but what exactly is Bitmain?
A Little Background
Bitmain was founded in 2013 by Jihan Wu and Micree Zhan, right as the first Bitcoin price surge was nearing its top. A lot of companies were getting into the mining game, but Zhan’s ASIC designs (I’ll talk about ASICs later) quickly put Bitmain on the map. Soon after, the Bitcoin price tumbled and put a lot of companies out of business. Bitmain held on.
When interest in the digital gold started to pick up again, Bitmain’s Antminer S5 was the best hardware available, and so became the majority favorite. And when it comes to computer hardware production, economies of scale often form.
This means that the bigger the company and more powerful their hardware, the faster the company can grow and improve. This can be seen with the major semiconductor company Intel, whose processors are running in nearly 70% of all computers worldwide. Once a lead has been obtained, it’s very hard to lose.
This head-start in quality and popularity gave Bitmain the boost to end up on top of the ASIC game, already achieving success on the scale of giants like NVidia.
In short, Bitmain is one of the largest cryptocurrency-related technology companies in the world, with massive influence and reach and a recent investment of $50million. Here we’ll break down what they do, how they help steer the crypto space as a whole, what role they may play moving forward.
Bitmain’s Different Roles
Bitmain is an umbrella company that operates as several companies with different goals that complement each other, together forming a crypto empire. The size and importance of these roles has led to several scandals throughout Bitmain’s rise.
Antminer: Mining Hardware
Bitmain’s primary role is as a producer of cryptocurrency mining hardware in the form of ASICs (very short for Application Specific Integrated Circuits). An ASIC is a type of computer that is designed to do only one job. In the case of Bitmain’s Antminer product line, their ASICs are capable only of mining cryptocurrencies, with various products for mining different coins like Bitcoin, Litecoin, Ethereum and Dash.

An Antiminer S9, Bitmain’s latest Bitcoin miner
Bitmain is by far the largest and most successful producer of ASICs so far, and they’ve recently released new Antminer models for mining Ethereum and Monero (though the Monero community is working to stay “ASIC-resistant”). Antminers are estimated to make up nearly 70% of all Bitcoin mining hardware.
The hefty market share that Bitmain enjoys is a natural result of them producing the most efficient and effective hardware, a distinction that will not be easily lost now that they’re entrenched. It also exposes a significant amount of the Bitcoin network to any bugs or security issues with the Bitmain hardware.
Antbleeding Out
Antbleed is a vulnerability in the Antminer software that allowed Bitmain secret access to shut the devices down remotely. This backdoor was revealed in April, 2017 and the massive portion of miners using Bitmain technology made the issue especially concerning. If exercised, Bitmain could theoretically shut down vast amount of the miners on the network and keep their miners running. This would allow them to effectively take over the Bitcoin network entirely, controlling the production of every block.
Antpool and Hashnest
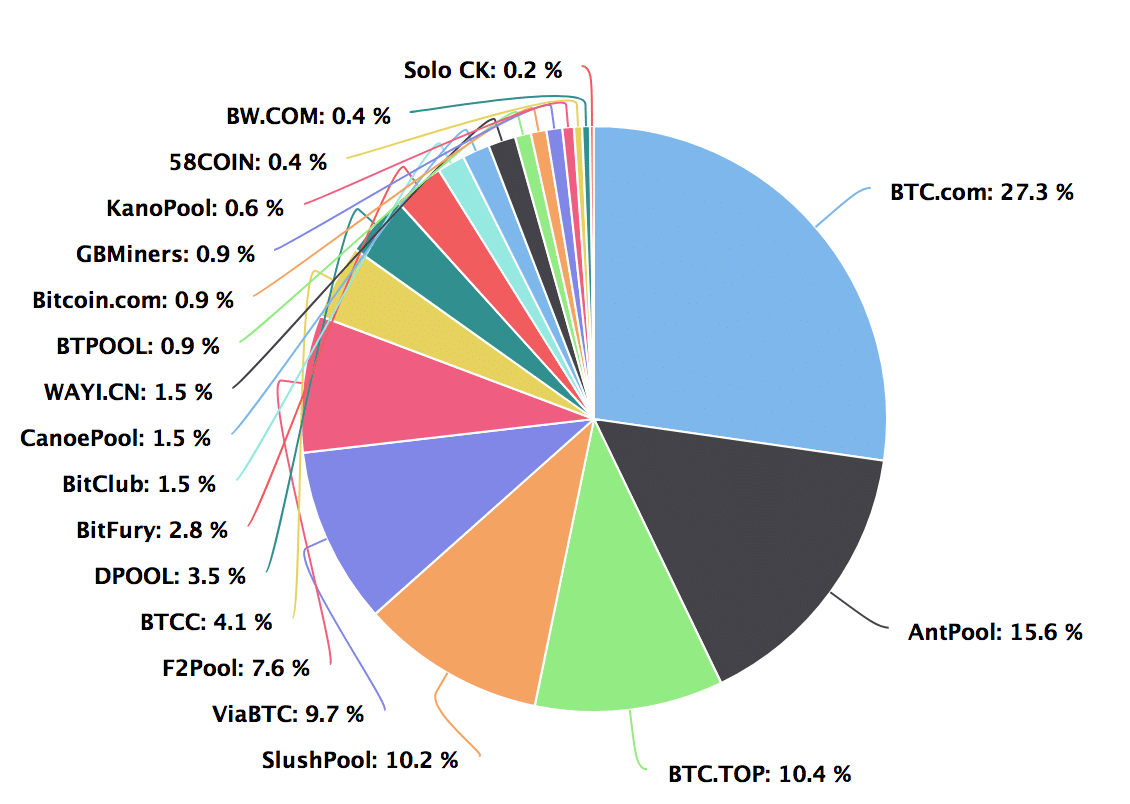
BTC Mining Hashrate Distribution as of April 14, 2017
Besides selling ASICs to help others mine, Bitmain also puts their technology to use mining for themselves and running mining pools.
Mining pools are networks of computers working together to mine for cryptocurrencies, sharing the rewards in proportion to each miners contribution.
Antpool and BTC.com, the two largest mining pools in the world, make up nearly 50% of the Bitcoin mining power. Both are owned by Bitmain, though how much of the computing power is their hardware as opposed to others contributing their devices is unknown.
Hashnest is a “cloud mining” service, which allows anyone to rent mining hardware from Bitmain similar to renting storage from Dropbox or server-space from AWS. These rented miners are maintained and operated by Bitmain on behalf of the renters and mine as part of Antpool.
While Bitmain may not directly own nearly half the network, they do control an oversized amount of influence over the voting activity of their own pools and other pools. Bitcoin protocol changes occur by nodes mining on the network “signaling” acceptance, or showing that they would support blocks with the new protocol format. This influence empowers Bitmain to attempt to control the direction of the Bitcoin protocol development.
Bitmain <3 AsicBoost
In April of 2017, around the time of the Antbleed scandal mentioned above, Segregated Witness and AsicBoost were both in the news. Segregated Witness (SegWit) was a controversial Bitcoin protocol change aimed at scaling the network. AsicBoost was a new innovation in Bitcoin mining hardware that allowed power efficiency boosts of up to 30%. However, SegWit and AsicBoost are not compatible.
Bitmain had been working on AsicBoost technology for some time, and there were those who believed the extra efficiency would make their already healthy share of the network even healthier, giving them more control. Bitmain was also a vocal opponent of SegWit, and accordingly their mining nodes and pools were set to reject the protocol upgrade.
Many in the community came out against Bitmain, accusing them of preventing SegWit in order to make more money using AsicBoost. Bitmain defended themselves from these allegations in a blog post. The real reason for their rejections of SegWit (as founder Jhan Wu told Bitcoin magazine) was to force a proposal they WERE a fan of, namely increasing the size of blocks via a fork called Bitcoin Unlimited.
Sophon: Artificial Intelligence Hardware
With mining fully in hand, Bitmain is looking toward the future and their next innovation. That innovation comes in the form of Sophon, a company offering specialized hardware aimed at artificial intelligence applications.
So far, Sophon offers ASIC processors that train neural networks instead of mine cryptos, specifically designed database systems for AI data, and even a personal AI-powered home robot that can play with your kids.
Bitmain and Sophon are some of the first to get into the game of building hardware specifically designed for AI, and expect to be running a fair share of the AI research ongoing currently in the next decade.
So Bitmain, like, owns Bitcoin?
Bitmain’s influence has only increased. As time goes on, we may see Bitmain using their weight to guide Bitcoin more and more. The combination of top-grade Bitcoin mining hardware production, massive mining operations, and mining pool operation make Bitmain the heaviest hitter when it comes to hashpower on the Bitcoin network. While they claim they have the best interests of the Bitcoin network at heart, only time will tell how they handle this great power and the responsibility that comes with it.
#DeleteBitmain or Not?
Bitmain is without a doubt a key player in the cryptocurrency space and in the computing space in general. They have yet (in my opinion) to show that they are truly bad-intentioned, but the possibility of an abuse of power is always there. Whether Bitmain retains their lead in the ASIC and mining realm remains to be seen.
What we can hope is that as adoption continues to increase, competitors will emerge to challenge their hold. Maybe you’ll start the next Bitmain, who knows.
The post What and Who is Bitmain? appeared first on CoinCentral.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.