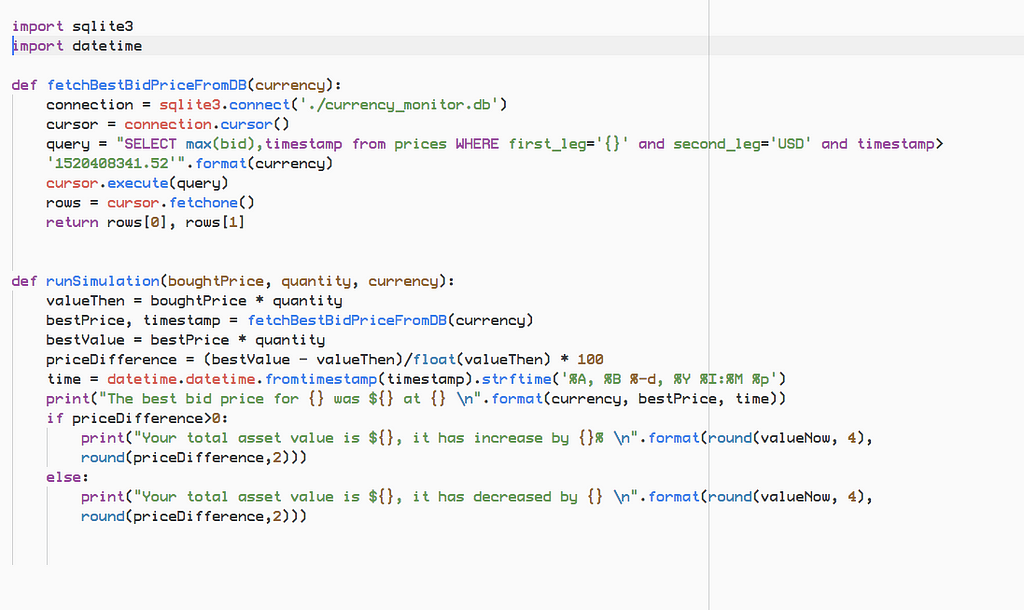
Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
 Learn to Code a Crypto Trading Simulator in Python
Learn to Code a Crypto Trading Simulator in Python
I am not a trader, but the whole idea of trading crypto is so tempting. I don’t want to invest real money unless I know what I am doing. I wanted someplace to test my strategies.
 Credits : xkcd
Credits : xkcd
So, I thought of building a Crypto Trading Simulator. The idea is to help beginner investor learn and experiment without losing real money. In this series, I will teach you how to build one. I have got a database which contains crypto prices of different exchanges between March 7th, 2018 and March 16th, 2018.
In this story, we will build a simple crypto simulator in python which allows the user to invest in a cryptocurrency, then we will run a simulator to see how the performance of his crypto asset in the next 9 days.
For now, we will display the best bid price for his asset, compare it with the initial investment and tell him if he made a profit or loss. In the coming stories, I will cover how to add live currency monitoring, how to write and test strategies, how to build the user interface, etc.. (I will need your support here, I have mentioned about the same at the end of the story.)
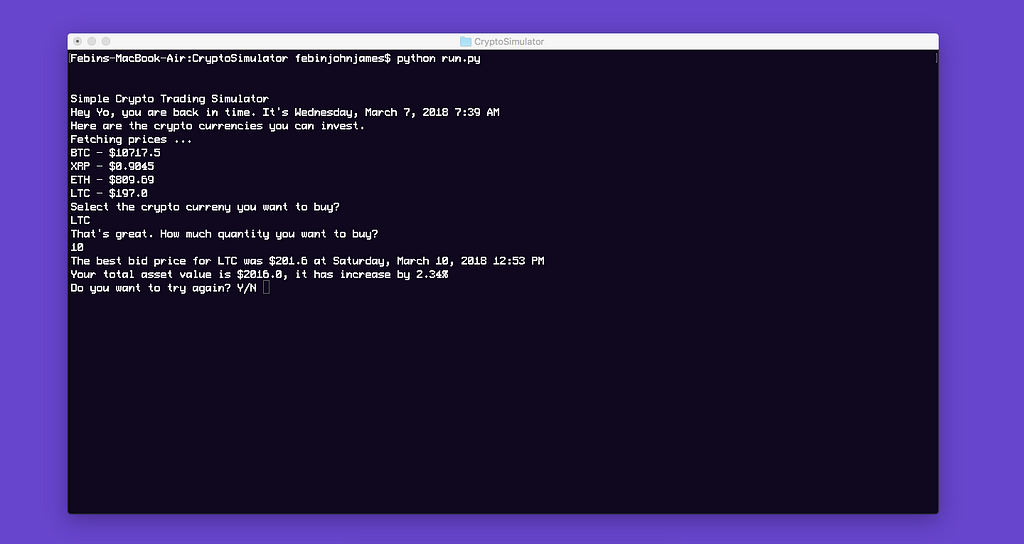
Here’s a video of the simulator we are building today, you can also take a look at the project’s Github Repository. You need to download the database separately from here and place it in the project’s directory.
Pseudo Code
Before we jump into coding, we need to have clarity on what are the next steps. This is important, otherwise we will often have confusions. We use pseudo code to get clarity, a pseudo code is not real code, but a roadmap in our own language.
Step 1: Welcome the user.
Step 2: We will fetch the cryptocurrency prices during March 7th, 2018 since our database starts at that time.
Step 3: We will ask the user to invest in one currency.
Step 4: Then, we will run the simulator to see how his crypto asset does in the next 9 days.
Step 5: We will find the best bid price for that currency, compare it with user's initial investment and display if he made a profit or loss.
We don’t have to do the steps in that order, we can do whichever is easier first. Because having more things completed gives us confidence and we are likely to complete the whole project.
The code used in this story uses Python 2.7 .
Let’s start by creating an empty folder, ex: “CryptoSimulator”. You also need to download the crypto price database from here and place it inside your project folder.
Make a file called “run.py”
 Credits : xkcdWelcome
Credits : xkcdWelcome
We will create a simple function called “welcome”. It does nothing great, just print a series of line, the program name, giving the user an idea of what the program is up to, in other words just saying “Hi”.
def welcome(): print(“Simple Crypto Trading Simulator”) print(“Hey Yo, you are back in time. It’s Wednesday, March 7, 2018 7:39 AM”) print(“Here are the crypto currencies you can invest.”) print(“Fetching prices … ”)
Great, now we need to fetch the prices of the crypto currencies at March 7 2018 , 7:39 AM.
Since our database is based on sqlite3, we need to download the python library, you can do that using the following command.
pip install sqlite3
Now at the beginning of the file run.py , we need to import the library.
import sqlite3
Now let’s write the code to fetch prices from the beginning of the time and display it.
In the database we have following columns, timestamp, first_leg, second_leg, ask, bid and the exchange name. If we consider the currency pair “BTC/USD”. The first leg would be BTC and the second leg is “USD”.
In the following lines of code, we are fetching the prices at a given time.
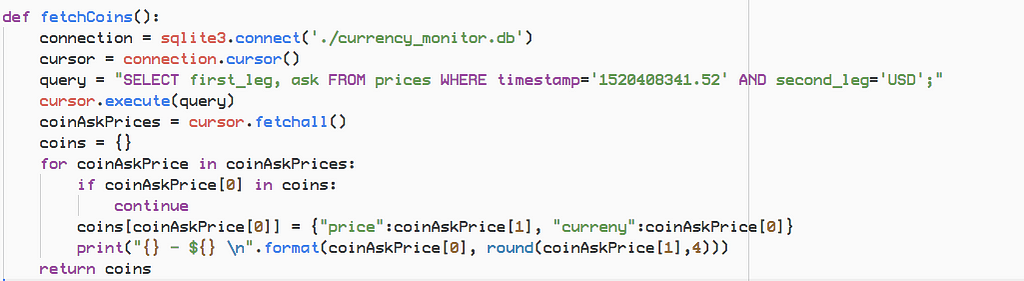
connection = sqlite3.connect(‘./currency_monitor.db’)cursor = connection.cursor()query = “SELECT first_leg, ask FROM prices WHERE timestamp=’1520408341.52' AND second_leg=’USD’;” cursor.execute(query)coinAskPrices = cursor.fetchall()
Now we will loop through the prices, remove duplicates, add then to python dictionary and print them.
coins = {}for coinAskPrice in coinAskPrices: if coinAskPrice[0] in coins: continue coins[coinAskPrice[0]] = {“price”:coinAskPrice[1], “curreny”:coinAskPrice[0]} print(“{} — ${} \n”.format(coinAskPrice[0], round(coinAskPrice[1],4))) return coinsIf you don’t understand the code, don’t worry. Just download the repository, run it and tinker around and see what happens, slowly everything will start to sense.
Now we will combine the above pieces of code into one single function “fetchCoins”.
 Credits : xkcd
Credits : xkcd
Now that, the prices have been displayed, we will ask the user which crypto he wants to buy and how much. We will create a function called “inputBuy”.
def inputBuy(): print(“Select the crypto curreny you want to buy? \n”) curreny = raw_input(“”).upper() print(“That’s great. How much quantity you want to buy? \n”) quantity = float(raw_input(“”)) return curreny, quantity
Now we need to find the price of the currency which the user is interested. We can simply do that by querying the python dictionary.
price = coins[currency][‘price’]
Then we need to pass these parameters to our simulator. Let’s put together these pieces of code into the main function.
Yes, the “runSimulation” function is not defined yet, we will be doing that next. We can do this another file, create a file “simulator.py”
 Credits : xkcd
Credits : xkcd
We need to import these libraries
import sqlite3import datetime
Now let’s define the function runSimulation.
def runSimulation(boughtPrice, quantity, currency): valueThen = boughtPrice * quantity bestPrice, timestamp = fetchBestBidPriceFromDB(currency) bestValue = bestPrice * quantity priceDifference = (bestValue — valueThen)/float(valueThen) * 100
Here we are are calculating the total asset price at the time of buying, then we are finding the best price for that currency during March 7th and March 16th. Later we are calculating the difference to find, if the value increased or decreased.
To find the best price, make a function called “fetchBestBidPriceFromDB”.
def fetchBestBidPriceFromDB(currency): connection = sqlite3.connect(‘./currency_monitor.db’) cursor = connection.cursor() query = “SELECT max(bid),timestamp from prices WHERE first_leg=’{}’ and second_leg=’USD’ and timestamp> ‘1520408341.52’”.format(currency) cursor.execute(query) rows = cursor.fetchone() return rows[0], rows[1]We also need to add few more lines in the runSimulation function to print our findings.
print(“The best bid price for {} was ${} at {} \n”.format(currency, bestPrice, time))if priceDifference>0: print(“Your total asset value is ${}, it has increase by {}% \n”.format(round(bestValue, 4), round(priceDifference,2)))else: print(“Your total asset value is ${}, it has decreased by {} \n”.format(round(bestValue, 4), round(priceDifference,2)))Let’s put these pieces of code together.
It’s almost done, but I want to add some drama. You know in the movies, the letters get printed one by one in the console?
Create a file called “drama.py” and add these lines of code
import timeimport sys
def dramaticTyping(string): for char in string: sys.stdout.write(char) sys.stdout.flush() time.sleep(0.10)
Now import this file on run.py and simulator.py, then replace the function call print with dramaticTyping.
Congrats, we have got a basic version of our crypto trading simulator ready.
Claps Please 👏 , Thank You 😊. This is only the beginning, we will do a lot of things in the coming series like integrating this with live crypto API’s, writing and testing strategies, making a UI, etc.
Follow us, HackerNoon and me (Febin John James) so that you won’t miss out on this series.
I need your support, if I get enough support, I will even build a mobile app and publish it for free. Please support me by buying me a coffee. You can also sponsor this series, please reach out to me on my Linkedin.
You can also donate cryptocurrencies.
BTC
3Bhk7F9Sg8uSnkvUYRMbWtAGybGccUfvDY
BCH
qr4eh8v33gxvseqqsx5y26zqqxd3gntqss4z7mu8vn
ETH
0xB65BBf5C47f9Abc2d40A5E739DD69c64C2e89A0f
How to Build a Simple Crypto Trading Simulator, Part 1 was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.