Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
With its highly composable lending and borrowing v2 platform, will Gearbox provide a liquidity renaissance to DeFi?

Gearbox protocol is a lending platform. But that statement is an injustice to the project as it is much more than that. The Gearbox docs put it best, stating that the protocol aims to be a leverage middle layer for DeFi. This is because while the main components of the protocol involve lending and borrowing, users can increase and decrease leveraged positions, swap between assets using their favorite DEX, stake in liquid staking positions, and soon enough, much more.
While documentation provided by the Gearbox protocol is already quite robust and the founder Ivangbi has recently explained many of the new improvements in his 33-page medium post, It can be easy to get lost in it all. For this reason, this article aims to provide a summary of the new Gearbox v2 to understand the protocol, some of its innovative features, and corresponding risks.
Brief Summary
Gearbox is a composable leverage protocol that allows under-collateralized borrowing. Borrowers can then deploy these leveraged assets into different DeFi protocols. The protocol is divided into two overarching components:
- Passive Pools: Single asset lending. Deposit into the asset pool and earn interest from borrowers plus rewards. When a user deposits an asset into one of the passive pools, they receive diesel tokens (dToken) of that asset. This asset earns interest and is redeemable for the amount of the underlying asset deposited plus interest.
- Credit Accounts: This is the borrowing side of the protocol. Users will deposit collateral to open a credit account which will allow them to borrow up to 10x from the lending pools. Users will then be able to swap borrowed assets for other assets or deposit into allow-listed pools (pools approved by governance) to earn leveraged yields.
Much of the lending protocol aspects of Gearbox are inspired by Aave, where both the lending and borrow rates are intertwined through the utilization ratio (total borrowed assets/total supplied assets) of the lending pools.
Interest Rates on Gearbox
Passive Pools
Passive pools are the supply side of the Gearbox Protocol’s lending market. The mechanics of the lending rates are nearly identical to that of Aave. Each asset pool supply rate has two slopes that revolve around an inflection point that is the optimal utilization rate of the pool determined by the protocol. The first slope increases the supply rate slowly as the utilization rate increases, Once the utilization rate has passed its inflection point, the rates increase substantially.
On the supply-side, Gearbox’s first initiative is to focus on blue-chip assets that have less volatility (in crypto standards). As of now it is possible to supply ETH, stETH, WBTC, and several stablecoins.
Credit Accounts
The borrow rates for credit accounts are where the protocol deviates the most from Aave’s lending model. Instead of a model revolving around the optimal utilization rate as an inflection point that has different slope rates before and after, they will implement a smoother curve that gradually increases the borrow rate as is seen below in the graph
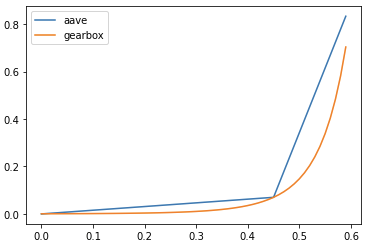
Source: Gearbox Colab Docs
The Innovative Credit Account
Each credit account will be denominated in the asset that is borrowed and will only be able to borrow this asset. However, multiple collaterals can be used in the same credit account. Users can also open multiple credit accounts, each with a different denominated asset. Collateral is isolated to each credit account and cannot be used across multiple credit accounts.
Homepage for credit accounts. Source: Gearbox site
Credit account users can swap the asset they borrowed for other allow-listed assets and then deposit these assets into allow-listed pools directly through the gearbox interface. Each credit account will have a portfolio summary that shows the assets held and the health factor of position. This added composability in credit accounts means that users can manage multiple strategies within one borrowed position. For example, a user wants to deposit into Curve’s ETH/stETH pool, but they also want to hedge against the risk of a large stETH price deviation to the downside. This user could use stETH as collateral and borrow more stETH. They could then add a portion of their total position into the Curve pool and swap a portion of the position into ETH or a stable coin that they leave idle in their credit account (or even deposit into the Curve 3pool if a stable coin). If a price drop for stETH occurs, they can disassemble their positions and repay their loan, profiting off of the price change.
Another innovation for advanced users is the multicall feature that is released in v2. The multicall function allows users to perform multiple transactions across assets and protocols in one transaction on one block. At the protocol level, this means that one-click strategies (see image blow) can be created that provide easy access for users to enter specific positions. At the user level, users would be able to develop their own multicalls to assemble and take apart positions quickly. For reference, the ETH/stETH hedging strategy mentioned above could be all done in one multicall.
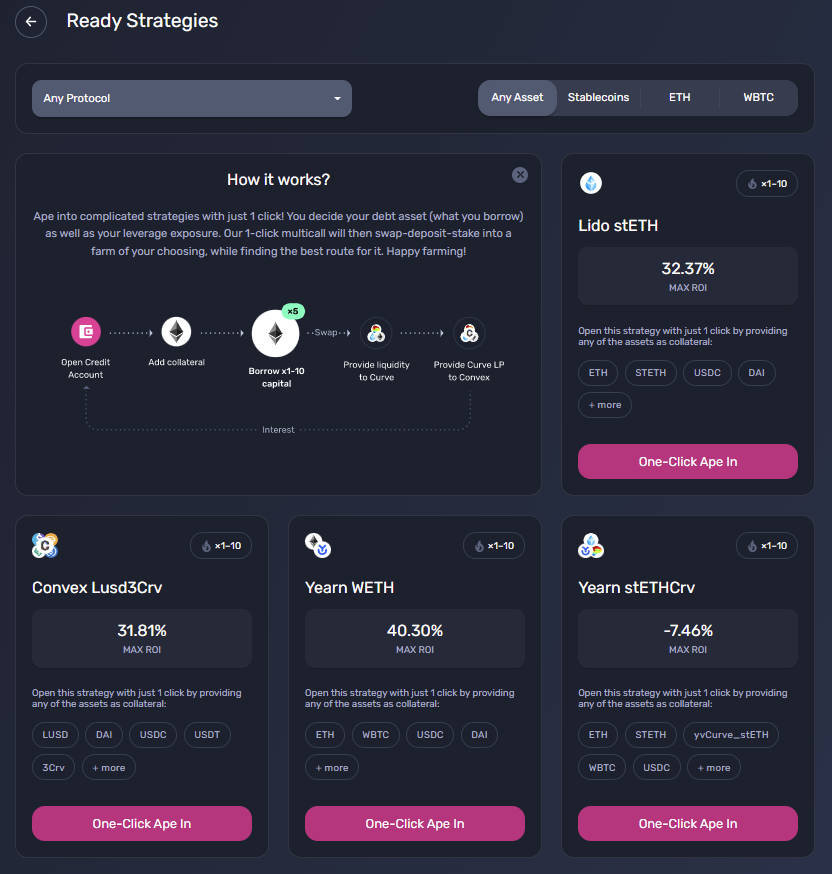
Screenshot of One-click strategies on Gearbox. Source: Gearbox site
Example Strategies with Gearbox v2
While an example of a more complex strategy hedging against the price of stETH is given above, Gearbox can also be used to leverage simpler and lower risk strategies to make their returns more appealing. A good example is deploying assets into one of the stable coin pools on Curve. An example seen in the charts below is the sUSD/DAI/USDT/USDC pool in Curve. The current returns (as of Nov. 4, 2022) depositing into this pool are as follows:
- Trading fees earned per dollar in the pool: 0.082%
- CRV rewards earned: 0.79%
- SNX rewards earned: 0.92%
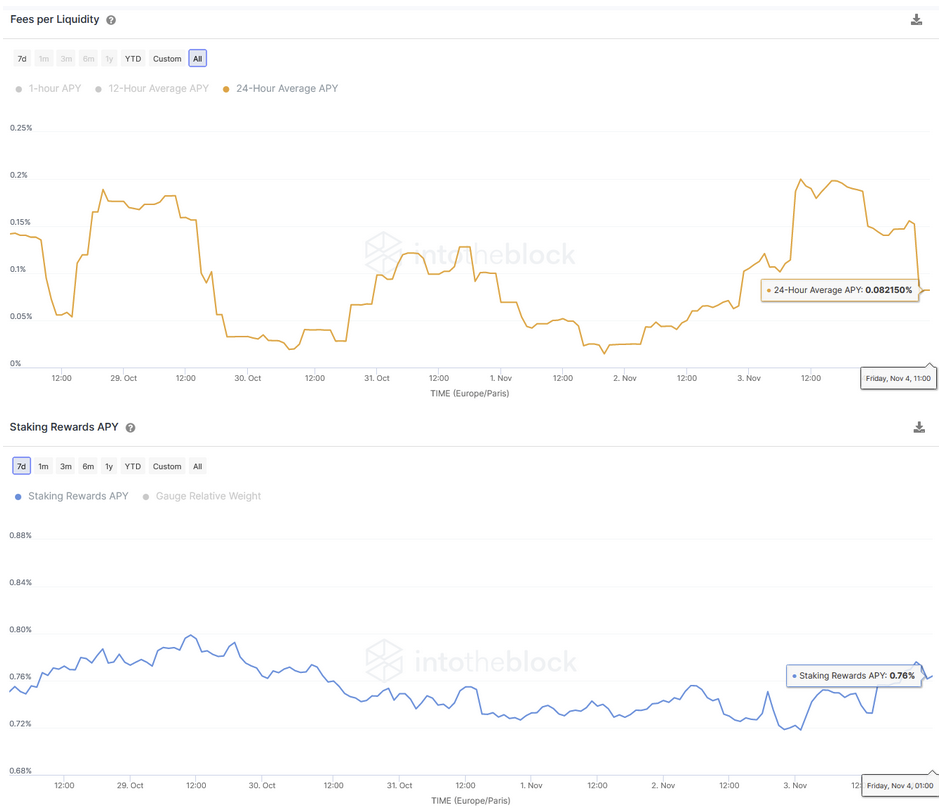
Source: IntoTheBlock Curve Protocol Indicators
The rates added up a depositor would earn in the pool amount to 1.79%. Through leverage on Gearbox, the returns rate can be as high as 17.9% using 10x leverage (not advised). At a more reasonable leverage of 7x, rates can still be as high as 12.54%. There are borrowing fees that will need to be paid in the Gearbox protocol, which will reduce these rates somewhat, but the potential to earn above 10% on stable coins is an appealing strategy given the current rates available in the market.
Liquidation Enhancements
With the multicall capability enabled from within a credit account, this has opened up a new dynamic on how to perform liquidations through Gearbox. Since all collateral and borrowed assets are managed through the credit account liquidators can perform liquidations without having to provide assets upfront. Instead, liquidators can build liquidation multicall functions that execute all transactions to clear the bad debt and take their profits in one block. This increases liquidity efficiency and can also reduce the costs incurred by the liquidator (no need for flashloans).
How it Differs from Similar Protocols
Composability is Golden
The main aspect that separates Gearbox from other similar protocols is the composability that it allows. Credit accounts in Gearbox can choose which asset they want to borrow and then are able to swap this asset with any other allow-listed asset on the protocol. This composability continues by allowing for multiple strategies to be executed and managed through the same credit account to give the credit account greater flexibility in its risk management.
Compared to Idle Finance
Funds used for leveraging in Idle Finance are isolated to each pool that is available in the protocol. Therefore, potential risks are enlarged for depositors into the Senior tranche if an exploit occurs in their pool. Isolated funding also puts senior tranche depositors at risk of not being able to withdraw their funds if the utilization ratio is too high and there is no mitigation method in place (such as rate curves). Since the Senior tranche funds need to also be deposited in the chosen strategy, they are exposed to economic risks of the strategy as well. Furthermore, leveraged borrowers in the junior tranche cannot adjust their leverage.
Compared to Alpha Homora V2
The first difference between Alpha Homora and Gearbox is the reduced flexibility in choice of what your borrowed asset is denominated in. This means that borrowers will have less control over their risk exposure. The second difference is that Homora only allows assets to be used in LP positions. This reduced composability also means that borrowers have less ability to manage their risks and are frequently exposed to IL without an easy method to mitigate it.
There is always risk…
The innovations in Gearbox v2’s leveraged borrowing design have the potential to unlock a lot of liquidity in the market. However, there are always risks with lending and leverage that are important to highlight.
An important dynamic to note for credit accounts is that the loan-to-value (LTV) is different for each asset depending on the pool’s denomination asset (what was supplied as collateral and borrowed when the credit account was opened). This means that having a predetermined strategy for each credit account can help mitigate risks. This also implies that swapping between assets within a credit account can have impacts on the health factor of the account and needs to be considered before execution.
Another added risk layer with highly composable borrowed positions is the difference between how the oracles used by Gearbox update their prices. A recent liquidation because of how prices are updated on the oracles used for ETH and stETH. For a user interested in implementing a complex strategy, it is important to review the oracles Gearbox uses and how prices are updated for each oracle.
The lending side of Gearbox has fewer risks, but there are still some risks to lending that are important to consider. The implicit assumption of using a credit account is that a user will deploy their leveraged assets to any number of the allow-listed pools on Gearbox. This means that the assets lenders provide are exposed to smart contracts in protocols outside of Gearbox. If an exploit happens on one of these protocols, there is a risk that the capital provided by the lenders will be lost.
Gearbox does have an insurance mechanism to maintain the value of their diesel tokens by using funds in their reserve if some event occurs where the amount a credit account repays is less than what they borrowed. However, it is unclear from their documentation if the reserves will also be able to cover large incidents such as an exploit.
On the Gearbox Horizon
Gearbox is still in its initial phases of v2. Anyone can add liquidity to the passive pools, but only confident degens willing to borrow a minimum of $100k can open credit accounts. As the protocol matures, the Gearbox team aims to add more protocols to their allow list. A feature in the pipeline that will further increase the dynamics of the protocol is for credit accounts to be able to hold non-fungible assets, such as Uniswap v3 positions. This will greatly increase the potential protocols and strategies that will work in the protocol.
Conclusion
Gearbox has spent a year testing in production to develop their new v2 protocol. The increased composability that Gearbox provides means that types of strategies on how to use leveraged borrowing will flourish. Furthermore, with these new strategies and how the leverage within the credit accounts is designed will unlock liquidity in assets that have lower yields or fewer applications in DeFi. The customizability of the borrowed leverage will be a boon for users that want to implement complex strategies and the multicall one-click strategies will be highly appealing to degens that want to get higher returns in DeFi.
There will also be benefits for protocols that are voted by governance onto Gearbox’s allow-list. The unlocked liquidity from the lent out assets will come flooding into these protocols
Gearbox is still in its infancy, but there is open-ended potential. When credit accounts become available to both small and large borrowers alike, an influx of liquidity in the protocol could have a cascading effect into other protocols that are available through Gearbox, potentially sparking a liquidity renaissance across DeFi.
Gearbox v2: A New Approach to Leveraged Borrowing was originally published in IntoTheBlock on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.