Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.

Often, difficult economic problems are seen as too sprawling and complicated to even understand, let alone solve. The problem of rising healthcare costs in the United States, in my view, deserves such a reputation. Good explanations of healthcare costs defy concision.
This is not the case with income inequality. There seems to be a relatively clear reason that wage differentials are so extreme in the U.S.: professional services wages. I’m talking about doctors, lawyers, and bankers.
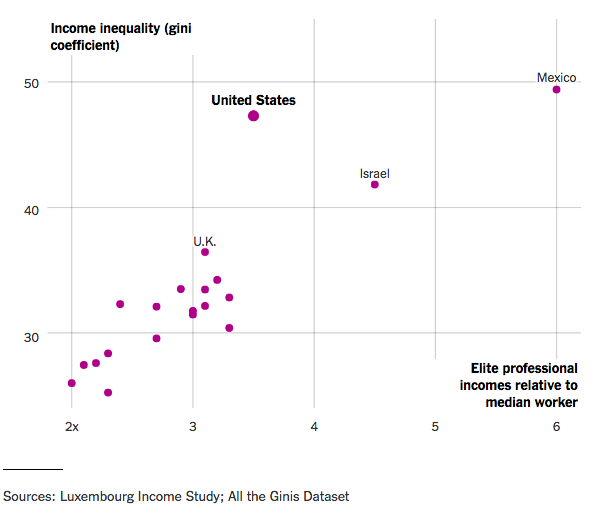
You can see it pretty plainly in this chart, which I lifted from a New York Times article. I’ve seen similar evidence several times recently. The main idea is the same: the top 0.1% is comprised of people who founded things, but the top 1% is mostly full of professionals.
This begs the question of why the U.S. tends to pay professionals so much. I don’t claim to know the answer. Perhaps part of the answer has something to do with the difficulty of competing in those industries. It is notoriously difficult to start a financial services company capable of competing with, say, Goldman Sachs. How about a new big law firm or a new big hospital? Very tough. Notably, software engineer salaries don’t usually make the cut for top 1%. Software has dramatically lower barriers to entry than the previous three industries.
I will single out financial services professionals for a moment: they are overpaid. Something is wrong. We shovel huge amounts of cash to people who “manage” and “analyze” assets. At best, they are lousy. At worst, they cause 2008. Society pays portfolio managers to do worse than nothing. Just stick your cash in the S&P 500 for 10 years and you’ll beat nearly every professional manager. Yet, the top 1% of earners is stuffed full of financial analysts. I feel this is mostly a product of public ignorance. If information in the market were flowing all the way down the pipes, the market would brutally punish financial services.
I can only guess, since I’m no expert, but there are likely large pockets of value being sequestered and tapped by doctors and lawyers.
Implications for New Ventures
This all has many implications, but my concern is for new ventures. It seems I’m not alone in my beliefs about the gross inefficiencies in the financial services industry. Some new products are starting to break down the barriers. Robinhood lets users trade stocks for free. Betterment is a portfolio management system that uses passive investment. Interestingly, Betterment is owned by Vanguard, a big financial services company. It seems even the incumbents are starting get a bit wise.
There are countless opportunities new startups in finance. It’s a huge industry, and there are still tons of hedge funds charging people to lose to the S&P 500. But at least a start has been made.
Startups are also nibbling away at the bloated healthcare industry. Carbon Health is an attempt to integrate the healthcare process and consumer technology (see your doc for follow ups via video call, get test results as push notifications, etc.) Intuitive Surgical and Mazor Robotics have both developed robotic systems for aiding in surgery. There are dozens more.
Legal services startups are perhaps the least developed of the three. TurboTax is, to some degree, the first breakthrough legal startup. LegalZoom is notable as well. But nobody has cracked the deeper levels of law, the stuff for which lawyers earn extremely high incomes. There are many possible reasons for this, but there is also probably a huge amount of potential.
A Different Model
I have a very simple idea. Typically, the approach to attacking all of these services is automation. Automating this stuff is very hard, and will take a long time. In the meantime, why don’t we start hiring people from the poorest countries to do the stuff that is hard to automate in these three industries?
It’s very easy: take X, a target of automation. Why are we targeting X for automation? Because it is taking up the time of a highly paid person. So let someone from Africa do X, pay that person double their local wages, and charge the end consumer less for the service. Everybody wins.
This can work in many, many areas. The main reason it doesn’t is because of regulatory barriers. But a clever person should be able to find pockets where the regulations allow it. That would be a great thing, in my view.
Hacking a Vice of the U.S. Economy was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.