Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.

The blockchain is born in the mind of Satoshi Nakamoto, a genius pseudonymous and unidentified creator of Bitcoin. Satoshi could be one person or a group of person.
Satoshi Nakamoto described Bitcoin in 2008 as “purely peer-to-peer version of electronic cash”
His motivation to create the blockchain was to replace the trusted third party.
How?
The blockchain is a public and secured database. This is a list of records of every entries and exits of information. The list is continuously growing.
It provides proof of who owns what at any given juncture. Moreover, this ledger is repeat on many computers, the Bitcoin’s nodes. The ledger is distributed all around the world publicly
The main difference of blockchain is: There is no financial middle man or central review body.
It means, there is no trusted third party in the process of a blockchain. The security of the system is guaranteed by its consensus mechanism, the system of network nodes who work and agree on how to update the blockchain when there is a new order of transfers from one person to another.
Let’s try to explain this complex concept with the Bitcoin example.
How does Bitcoin Work?
Who give what to who?
James want to send money to Mary.
First, they both need to have bitcoin “wallets”. It’s a software that allow you to access to blockchain. It can be compared to a browser for Internet. A wallet to Bitcoin is like a Mozilla Firefox to Internet, an access door.
Then, James uses his cryptographic key to order the transaction. A cryptographic key is transforming plain text into cipher text or vice versa. The key is private and ensures secure communication. This is the core part of cryptographic operation.
Mainly, James’s wallet is asking to change the blockchain by taking money from his wallet to put it in Mary’s wallet.
His order is joining others orders in a block, containing cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp and a transaction data. This means that a block is linked to others blocks and can’t be modify separately.
Why?
Because, a blockchain is a decentralized, distributed and a public ledger. It records transactions on many computers. So if you try to change a record retroactively, it would change several blocks and corrupt the all network.
Back to our transaction, James is making his order. The order join the network to be analyzed by the various nodes. They inspect the ledger to check if James really has the bitcoins he wants to spend.
If everything is ok, specialist nodes, called miners, will pack james’s order with others similarly transactions to create a new block.
The block is time marked with a date and it’s added to a blockchain and join the network.
Finally, Mary receive the money from James
To resume:
1. James want to send money to Mary.
2. His order is joining others orders in a block
3. The order join the network to be analyzed by the various nodes
4. The block is time marked with a date and it’s added to a blockchain and join the network.
5. Finally, Mary receive the money from James
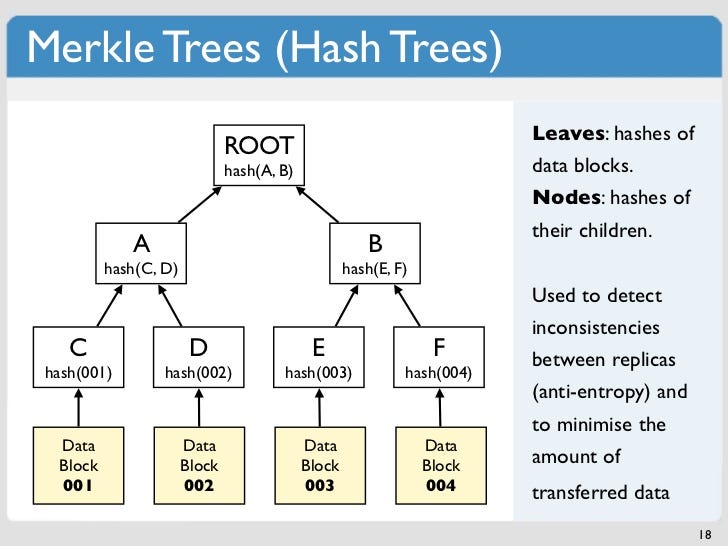
During the process, each transaction makes a hash value. This hash value is the record that will be bound with others hash value in order to form the block. The schema of all the transactions and hash values used to create a block is called a “Merkle Tree”.
Here is the process of a bitcoin transaction. The blockchains are built to add score of new blocks onto old blocks. Blockchains don’t overwrite on old blocks, they extend with the record of the new blocks in order to secure the whole system.
This operation is called mining and it is mainly done in mining pool. The first Bitcoin mining pool was Slush Pool. It’s advanced yet also great pool for beginners.
We see that the blockchain technology allows to make transactions without any central review body.
So it may be a great opportunity for the governed to take some power back on their money to the governors.
But…
How to make sure that James has the bitcoins he wants to transfer to Mary?
Every record in the blockchain is public and every blocks are linked by cryptographic hashes, timestamps and transaction data. So James transaction history is public and can be check during the process. And every bitcoin transaction can be tracked by the network hubs. Simply put, it is possible to know every transactions of every bitcoins on the network.
How to make sure that James will only spend these Bitcoins once?
Blockchain are secure by design. The principle of the Merkle tree and the nodes, the interdependency of the blocks and the extension of record instead of overwriting allows the blockchain to track every in and out of Bitcoins since the beginning.
Theoretically, it seems impossible for James to spend his Bitcoins twice.
Without trusted third party, where James’s and Mary’s wallets are stored?
Everywhere! The ledgers are distributed publicly and they are replicated on thousands of computers all around the word.
It means that the balance of your wallet is not stored in one place but in thousands of places to insure a high level of security.
A short video to explain with pictures the blochain concept
What a topic ! So many questions come to my mind after writing this story…
Is Blockchain the future of any transactions?
Are the banks dead?
Is Blockchain the future way to secure the anonymity of every transactions?
How Blockchain could save or ruin the world?
Why Bitcoin is a stupid investment?
Why mining pool concentration is the Achilles heel of Bitcoin?
Fascinating questions for our future and our children future!
As a committed citizen, I will invest on those questions and I will give an honest and documented answer for each one of them.
Thank you for reading. I hope it help you to see through this controversial topic.
If you like it, share it with your friends.
Always be clappin’
Kind regards.
Alexandre
Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency based on a blockchain! But how does it work? was originally published in Hacker Noon on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.