Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.
Mirror Protocol is a decentralized blockchain-based protocol that allows users to trade tokenized synthetic assets on the Terra blockchain; each synthetic asset on Mirror represents a real-world asset, such as stocks, such as NFLX or TSLA, or a commodity, like wheat or gold.
Hosted on the Terra blockchain, the Mirror Protocol can be used for various cross-chain and multi-chain operations, connecting ecosystems such as Cosmos, Ethereum, and Polkadot.
Mirror was designed with two goals in mind:
- It enables global users to trade US equities 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. Most trading platforms are limited to equities available in certain geographies. Mirror Protocols can be used by anyone anywhere, significantly reducing the barriers to entry to the specific financial markets.
- Instead of owning the real asset, users can manage and trade a tokenized version of an asset through synthetic alternatives.
Users searching for Mirror protocol will find two options at https://www.mirror.finance/. Users can click on either option to access Mirror’s app.
The native Mirror Protocol token, MIR, offers several utilities, most of which revolve around governance– MIR can be staked for voting rights. With most financial markets entrenched with the interests of large multi-billion dollar corporations, MIR places the governance of its synthetic trading market within reach for anyone willing to hold MIR.
Mirror Protocol is not without controversy. In September 2021 Terraform Labs CEO, Do Kwon, was handed papers ordering compliance with investigative subpoenas based on the U.S Securities and Exchange Commissions’ (SEC) investigation.
In retaliation, Kwon sued the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in December 2021. He stated the SEC had violated its own rules and the Due Process Clause of the U.S. Constitution. In February 2022, Kwon was ordered by a U.S. District Court judge to comply with the subpoenas.
How Does Mirror Protocol Work?
Mirror Protocol is hosted on the Terra Blockchain. It’s powered using smart contracts that allow its user base to trade commodities, stocks, and a range of other financial assets. It also lets users create a range of synthetic assets that represent the real-time and real-life value of the asset.
Through Mirror, investors can gain (or lose) from a real-world asset’s price fluctuations without ever actually owning it.
Terra runs on a Delegated Proof of Stake (DPos) consensus, and allows developers to build their own decentralized applications, protocols, and software.
Mirror Protocol combines DPoS with an open-source framework that builds multi-asset public Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains known as Cosmos SDK. This lets the protocol provide a range of tools to create synthetic assets, also known as “mAssets”. Users can create a position on the protocol to produce their own synthetic assets that mirror the value of their real-life alternatives. Once completed, users then need to deposit collateral. The system will then regulate all collateral supply to reduce the risk for lenders and ensure there are always enough funds to cover any mAssets.
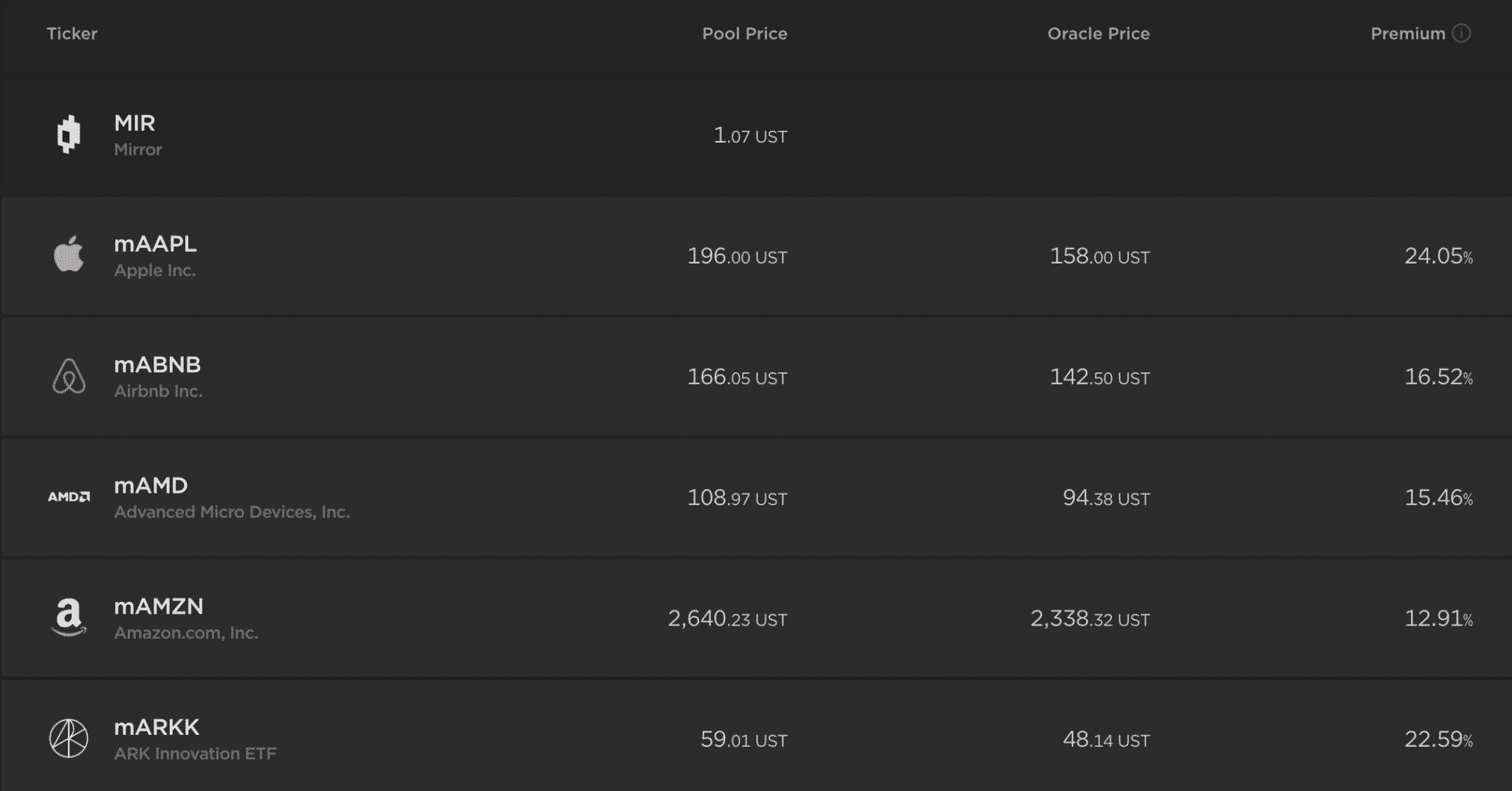
Once an mAsset has been created, it’s listed against UST (Terra’s dollar-pegged stablecoin) on the Terraswap platform. Mirror Protocol also helps to add liquidity to the network, including the swapping of tokens. Users who secure the network are rewarded with Mirror Tokens (MIR), which can be used for governance, trading, and several other activities.
One of Mirror Protocol’s unique value propositions is that it essentially opens local markets into global audiences. This is incredibly valuable for many developing economies hosting increasingly financially empowered populations.
These potential investors are typically limited to the platforms and investment vehicles in their own country, which are limited.
By using Mirror Protocol, in theory, they can own a token that represents actual financial assets without needing to buy them from a foreign exchange. This system helps lower the barriers to entry for traders, whilst also giving traders the opportunity to invest 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
Each mAsset is designed to be as transparent and accessible as possible. Through smart contracts, a synthetic asset can be made for any real-life asset, which can then be traded by anyone.
Mirror users can also add liquidity to the platform and earn rewards in the process, such as MIR tokens.
MIR can then be used to direct the governance of the platform, or sold on the open market.
Who Are the Founders of Mirror Protocol? A Brief History of Mirror
Mirror Protocol was founded in 2020 by the same team that developed Terraform Labs.
Based in South Korea, Terraform Labs has launched or incubated projects such as Chia, a mobile payments rising star, Terra (UST and LUNA, two tokens currently in the top ten largest cryptocurrency market caps), and Mirror.
Terraform Labs CEO and co-founder Do Kwon is a Forbes’ 30 under 30 Asia list recipient, and has attracted investors such as Binance, Arrington XRP, and Polychain Capital for Terra.
Despite being founded by a centralized company, Mirror Protocol itself is completely decentralized, run entirely by MIR holders, who use their tokens to vote on new proposals and fees on the platform. In alignment with fair distribution and decentralization, MIR tokens were not pre-mined and are fairly distributed among network participants according to their role in the protocol. This gives users a say on the governance of the platform.
The team aims to make access to the financial market easy through the creation of synthetic assets.
Kwon himself has recently been pressured by U.S regulations to provide testimony after SEC attorneys stated they believe enforcement action may be warranted against Terrorform Labs, linking Mirror Protocol with its founding company. As a resident of South Korea, Kwon has contested the subpoena and filed a lawsuit against the SEC stating that a Korean company is not liable to comply with U.S regulations.
The MIR Token (MIR)
The Mirror token (MIR) is Mirror Protocol’s governance token. It was designed to be fairly distributed amongst investors and therefore there were never any pre-sale or investor tokens. MIR is rewarded to investors who uphold the stability of Terra. The token itself has two main features:
- Firstly, it captures collateralized debt position (CDP) closures. Once a Mirror CDP has been closed, 1.5% is taken as a fee. These fees are used to purchase MIR tokens on Terraswap, which are then paid to anyone staking MIR.
- Second, protocol governance. Mirror tokens play an extremely important role in the protocol. They can be used to change several parameters such as the trading fee rate and the position free. In addition to this, it’s used to make spending proposals against the on-chain community pool. This pool holds MIR tokens that are used to advance the protocol. For example, funding developer grants and adding additional incentives to the protocol.
At launch, 18.3 million MIR tokens were airdropped to LUNA stakers and individuals who held UNI. This was to reward individuals for upholding the financial stability of Terra and display the potential of the project. Individuals who staked LUNA received MIR on a pro-rata basis and each UNI holder with over 100 tokens received 220 MIR.
The Mirror team also plans to launch an additional 18.3 million MIR tokens throughout 2022. These will be distributed to LUNA stakers on a weekly basis.
Liquidity miners now have the option to farm Mirror tokens by providing liquidity on Uniswap, Ethereum, and equivalent pairs on Terraswap. This is similar to how yield farming works on Uniswap.
All liquidity providers are rewarded over a four-year period, with rewards decreasing by 50% until the end of the final year.
With MIR tokens playing a key role in the governance of the protocol, Terraform Labs has decided not to keep any of its MIR tokens for a profit. The goal is to keep the project decentralized from its onset, and to ensure all rewards go to the community. There are no admin keys or senior access portals. Any changes made to the protocol must be made using MIR tokens throughout the community. For a governance proposal to pass, it requires majority approval of all Mirror token holders and will take a week to implement once passed.
Today, MIR can be purchased on a range of exchanges such as Binance, Coinbase and Crypto.com.
It can also be purchased on decentralized exchanges such as SushiSwap and PancakeSwap.
It can be purchased on most popular exchanges such as Coinbase, using fiat currencies such as USD, CAD, AUD, EUR, GBP, etc, or other popular cryptocurrencies such as BTC and ETH. Once purchased, it’s compatible with a range of wallets such as the Ledger Nano S and Trezor One, as well as MetaMask and Trust Wallet.
Final Thoughts: Is Mirror Protocol Legit?
Mirror Protocol is an exciting new DeFi project tackling financial opportunity inequality. It provides individuals in less developed countries access to financial assets that would otherwise be limited to a select few traders. This opens a world of opportunity to its users and also gives the project potential to scale with the new market.
It’s built by a team of trusted developers in an ecosystem poised for significant growth. Terra has thus far showcased a strong ability to support various DeFi dApps and protocols with a wide variety of use cases.
However, synthetic assets don’t come without their limitations. Although investors can own a replica of an asset, they’re never granted ownership of the underlying asset. This means they’re unable to obtain votes, access to dividends, or shareholder rights.
The post What Is Mirror Protocol? A Beginner’s Guide & What You Should Know appeared first on CoinCentral.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.