Latest news about Bitcoin and all cryptocurrencies. Your daily crypto news habit.

The Inter-blockchain Communication protocol (IBC) is one of the world’s largest and most important interoperability protocols. As of today, IBC has connected more than 40 chains and, in the last 30 days, processed more than 12M unique transactions. This makes IBC by far the largest interoperability protocol by almost any measure.
One thing you might have missed about IBC, however, is that it also plays an essential role for enterprise.
With funding from Interchain Foundation, Datachain has contributed to the Cosmos/IBC community with the goal of increasing the number of blockchains communicating with IBC. The focus of Datachain has been mainly on implementing IBC modules for various chains such as Hyperledger Fabric, Hyperledger Besu (Enterprise Ethereum) and Corda.
We believe that IBC is the best option to achieve interoperability between heterogeneous blockchains. Not only have enterprise partners such as NTT Data and JCB implemented IBC, but also governments like BSN (Chinese government blockchain platform) and USDF (United States banks-backed stable coin) have either adopted or are considering adopting IBC.
This article will explain why IBC is important in the enterprise space for everyone interested in blockchain interoperability.
Interoperability Requirements in the Enterprise
There are a number of baseline requirements for enterprise interoperability:
- The ability to connect multiple heterogeneous blockchains and apply it to various use cases
- Trustless interoperability
- Use proven technology and avoid vendor lock-in
The ability to connect multiple heterogeneous blockchains and apply it to various use cases.
Because digital assets and digital currencies exist on multiple blockchains, it is necessary for enterprise users to connect all (or many) of them to unlock and maximize all use cases.
Over the past few years, enterprise companies have built, or have started building blockchain-based services, and the platforms they use are different for each project. For example, Hyperledger Fabric, Hyperledger Besu, and Corda are commonly used in the enterprise space.
Moreover, some use cases require connecting enterprise blockchains to public blockchains such as Tendermint. For example, JCB has tested PvP (Payment versus Payment) settlements between Hyperledger Fabric and Tendermint chains using IBC, to demonstrate exchanges between digital currencies on each blockchain.
Since combining all enterprise and public blockchains into a single chain is unrealistic, it is necessary to connect these various chains to expand the utility of blockchain technology.
Trustless Interoperability
Some projects set up intermediaries that help achieve interoperability, but this runs contrary to the primary paradigm of blockchain — decentralization and the removal of gatekeeping third parties. Ideally, when an enterprise blockchain connects to a public blockchain, it is best practice to avoid putting an additional trust layer between them.
Additionally, intermediaries require transaction fees which increases costs and can become cost prohibitive due to the high-security standards required (equivalent to that of large financial systems). Therefore, achieving trustless interoperability is also essential.
Use proven technology and avoid vendor lock-in.
Enterprise companies looking to future-proof their tech, generally prefer proven technology and try to avoid vendor lock-in. This maintains flexibility and builds interoperability into their systems for the long-term. Therefore, it is preferable that applications open-source software in production.
Why IBC in Enterprise?
Circling back to the main theme of “why is IBC so important to the enterprise space?” Simply put, IBC meets all interoperability requirements for enterprise use cases of blockchains. But, how does IBC meet those requirements and why does it have an essential role in enterprises?
IBC is / provides:
- Trustless
- Support for Heterogeneous Blockchain
- Customizable On The Application Layer
- Proven Technology
1. Trustless
IBC connects blockchains trustlessly. With IBC, relayers pass packets between blockchains and, because each blockchain (not relayers) validates the other blockchain’s status via a light client, there is no need to trust the relayers. In other words: no additional trust layer is required.
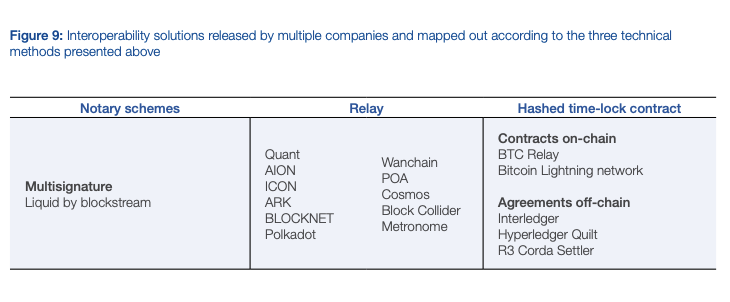
Source: Inclusive Deployment of Blockchain for Supply Chains: Part 6 — A Framework for Blockchain Interoperability — World Economics Forum
* According to the report by the World Economic Forum, this architecture is referred to as the “Relay” method.
In the Relay method, IBC has advantages in its unique specification by establishing a direct channel between modules on both ledgers, thus preventing communication between unrelated modules. It also has a mechanism to avoid further communication using the channel when the light client detects misbehavior.
2. Support for Heterogeneous Blockchains
Some people say IBC is only for Cosmos blockchains, but this is not true. Any blockchain with flexibility in smart contract features can communicate using IBC. And, developers in the Cosmos/IBC ecosystem have implemented IBC modules for a number of blockchains to connect with IBC.
https://ibcprotocol.org/lightClients/
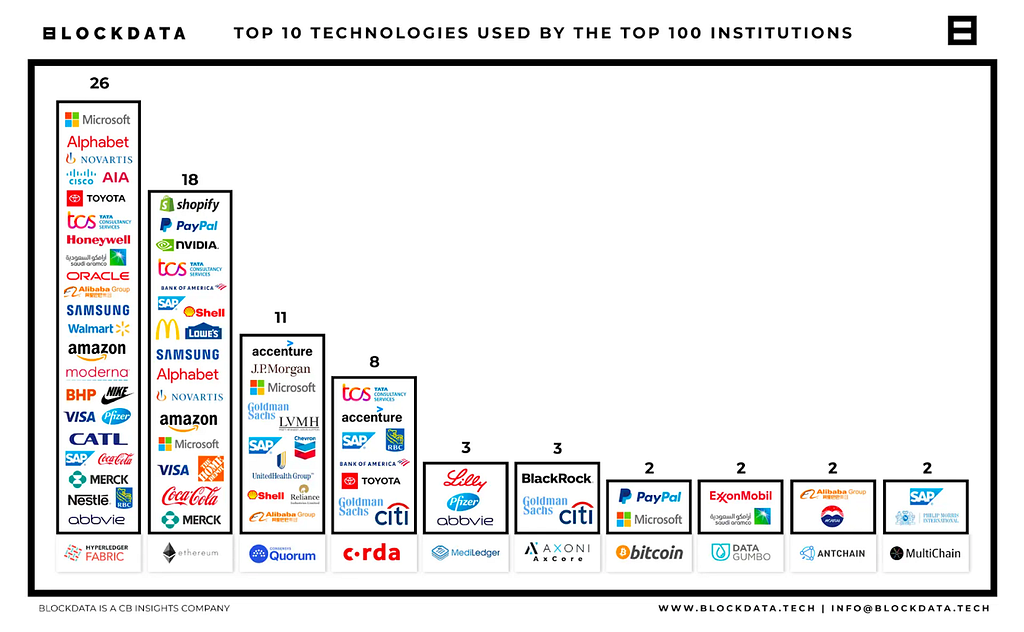
Source: 81 of the Top 100 Public Companies are using blockchain technology — BLOCKDATA
In the enterprise space, according to the research by BLOCKDATA, the most frequently used blockchain platform is Hyperledger Fabric. However, there are a variety of blockchains used by enterprise companies as described in the graphic above. Therefore, any interoperability protocol to connect those blockchains must be blockchain agnostic.
Datachain has implemented IBC modules for Hyperledger Fabric, Ethereum, Corda, Hyperledger Besu, and Hyperledger Iroha as a project called YUI (a Hyperledger Labs project). For more information about YUI, visit: https://github.com/hyperledger-labs/yui-docs
3. Customizable on the Application Layer
IBC is a protocol for the transport, authentication, and ordering of data packets between chains. It is not a single-use protocol designed for specific cases (e.g. atomic swaps).
Application developers can, therefore, build a multitude of cross-chain applications such as cross-chain token transfers and multi-chain smart contract applications. IBC manages communication so developers can focus on building applications.
4. Proven Technology

Source: Map of Zones
According to the Map of Zones, the number of blockchains (zones) connected via IBC is over 40 (as of this writing), and IBC has supported over 12 million transfers in the past 30 days. There is no other interoperability protocol in the world that approaches this level of transaction volume.
Connecting multiple blockchains in a trustless way is not easy, but IBC has proven it’s possible. This fact has attracted enterprise companies to adopt IBC to their systems.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the IBC protocol is beneficial not only to public chains but also for the enterprise use case because IBC meets all requirements of blockchain interoperability.
On top of that, since there is a strong need for interconnection between enterprise blockchains and public chains, IBC usage in enterprise space will promote IBC transactions in public chains.
Datachain is committed to building an interconnected world of public and enterprise blockchains — the Interchain, powered by the IBC Protocol. Our work on the YUI project continues and we look forward to collaborating with the ICF and Core Teams to drive adoption and scale communication throughout the Ecosystem. To learn more about building the Interchain together, Datachain can be found on Twitter and messaged here: contact us.
↓ We’ve published the second part of the article. The post below covers enterprise use cases using the IBC protocol.
IBC Use Cases in the Enterprise Space are Coming
Why Cosmos IBC Takes an Essential Role in the Enterprise Space was originally published in Cosmos Blog on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.
Disclaimer
The views and opinions expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not reflect the views of Bitcoin Insider. Every investment and trading move involves risk - this is especially true for cryptocurrencies given their volatility. We strongly advise our readers to conduct their own research when making a decision.